



Beyond The Red Black and Green: The Palestinian Thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women.
The diversity within traditional Arab women’s attire mirrors the vastness of the Arab lands spanning two continents, Asia and Africa. However, contemporary portrayals in popular media limit non-Arabs’ exposure to just a handful of these styles much like the Arab cuisine that has been simplified to ‘shawarma’ and ‘hummus,’ overshadowing its rich variety. Today Arab dress is often narrowed down to the ‘thawb Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. ,’ also known globally as a caftan, and ‘burqa’ for women, ‘kandura,’ and ‘guthra‘ for men.
Across the Fertile Crescent, North Africa, and the Mediterranean region, over centuries, a plethora of Arab costumes have emerged, each with its unique style serving specific purposes. These costumes have evolved over time, influenced by a variety of factors. Today, the diverse range of Arab attire differs from country to country and region to region, reflecting a culmination of collective experiences in their authentic forms. From Lebanon to the UAE, and from Sudan to Morocco, the variations in Arab costumes and their accompanying stories are both fascinating and enchanting. This paper aims to examine Arab costumes, with a specific focus on Palestine, delving into their characteristics and analysing their significance within the region.
Thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. a Palestinian perspective
The traditional attire worn by Palestinian women is commonly known as a “thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ,” also referred to as thawb Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. , tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. , and various other regional dialect variations across the Arab world. This garment, characterized by its loose tunic with long sleeves, is worn by both men and women throughout the Arab world, spanning the Middle East and North Africa, and occasionally in East/West Africa and parts of Iran. Interestingly, the term “thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ” originates from the Arabic word “thawb Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. ,” meaning fabric, signifying both garment and fabric in Arabic. For consistency and regional clarity, we will use the spelling “thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ” throughout this article.
Ideally, these garments can also be categorized into various types. While some may be referred to as “thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ,” others might be classified as “fustan
Fustān: (Greek: fustanella – a traditional pleated skirt worn by men along the Mediterranean and Balkan regions; Synonym: nafnūf, kurtah
Kurtah: (Cl. Persian: kurtah – long collarless shirt; Synonym: nafnūf, gawan, fustān), a garment generally for women worn in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia with a defined waistline and a full skirt with or without pleats. Gawan: (Eng: gown – an ankle length women’s garment with a full skirt; Synonym: nafnūf, kurtah
Kurtah: (Cl. Persian: kurtah – long collarless shirt; Synonym: nafnūf, gawan, fustān), a garment generally for women worn in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia with a defined waistline and a full skirt with or without pleats. Qumbāz: (Arabic; Synonyms: sayah
Ṣāyah: (Classical Persian: sāya – shadow; Synonyms: zubūn, qumbāz, gombaz, yalak
Yalak: (Ottoman Turkic: yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. – a hip or waist length vest; from Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest), a short-sleeved waistcoat traditionally worn by men and a long outer robe or tight jacket either sleeveless or short sleeved with a tight bodice traditionally worn by women in the Ottoman controlled Levant. Yalak: (Ottoman Turkic: yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. – a hip or waist length vest; from Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest), a short-sleeved waistcoat traditionally worn by men and a long outer robe or tight jacket either sleeveless or short sleeved with a tight bodice traditionally worn by women in the Ottoman controlled Levant.
The distinctive feature that distinguishes a Palestinian garment from other traditional attires in the Arab region is its intricate embroidery. Palestinian garments are adorned with elaborate cross-stitch embroidery, commonly known as fallahi Fallāḥī: (Arabic) Palestinian style cross-stitch embroidery. Literally means ‘farmer,’ because the art form was widely practiced in the rural farming communities of the south and central regions of historic Palestine., often executed in vibrant red silk floss Floss: (Old French: flosche – nap of velvet), is a type of silk fibre obtained from the cocoons of wild silkworms. It is characterized by its long, fluffy fibers that are not tightly woven, making it ideal for use in various textile applications such as embroidery, lace-making, and sewing. thread. The key identifier of a Palestinian garment lies in the arrangement and style of its embroidered panels.
Interesting fact: The Arabic term for cross-stitch embroidery, ‘fallahi Fallāḥī: (Arabic) Palestinian style cross-stitch embroidery. Literally means ‘farmer,’ because the art form was widely practiced in the rural farming communities of the south and central regions of historic Palestine.,’ originates from the word ‘fallah,’ which means peasants or farmers, reflecting its historical association with women from rural communities. However, in modern usage, it is sometimes erroneously replaced with the term ‘ṭaṭrīz.’ The latter is actually the Arabic term for embroidery. This confusion arises because ‘ṭaṭrīz‘ is often mistakenly identified with cross-stitch or ‘fallahi Fallāḥī: (Arabic) Palestinian style cross-stitch embroidery. Literally means ‘farmer,’ because the art form was widely practiced in the rural farming communities of the south and central regions of historic Palestine.’ embroidery, prevalent in Palestinian and Levantine traditions.
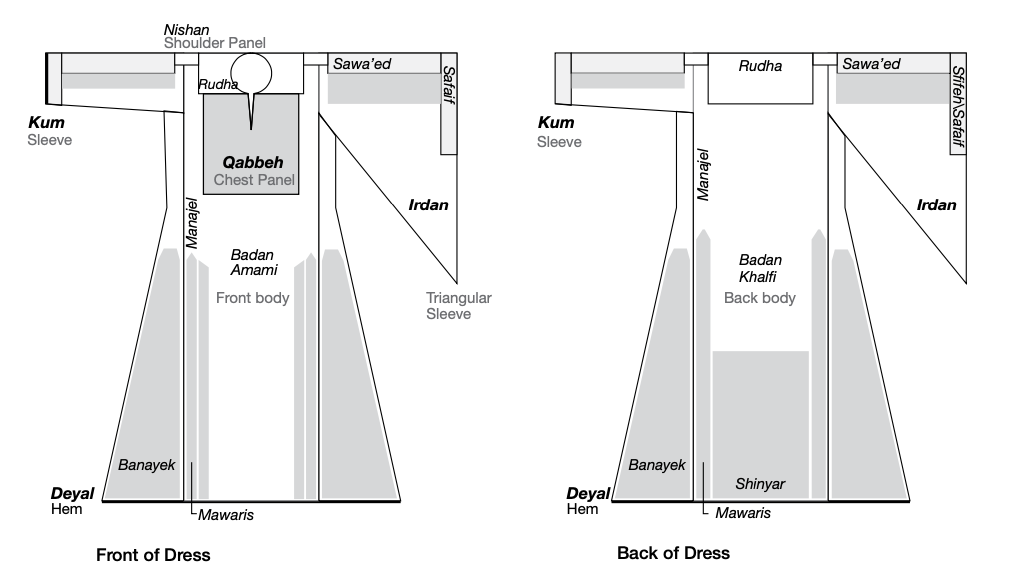
The above diagram from the book Palestinian Embroidery: Traditional Fallahi
Fallāḥī: (Arabic) Palestinian style cross-stitch embroidery. Literally means ‘farmer,’ because the art form was widely practiced in the rural farming communities of the south and central regions of historic Palestine. cross stitch by Widad Kawar illustrates the typical placements of embroidered panels commonly found on Palestinian thobes. While each panel holds significance with its distinct name, the most crucial ones include the chest panel, known as the ‘qabbah
Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan) Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan)
The other important identifiable symbol of a Palestinian thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. although not unique to Palestine today is the embroidered seamlines or ‘manajil.’ It is believed that the art of creating ‘manajil’ has been a tradition among women in the Middle East, particularly in the Levant region, for centuries. Interestingly, this technique is also widely practiced among Native Mexicans, who attribute its origins to their Spanish conquerors. It’s plausible that the technique was introduced to the Spanish diaspora by the Umayyad Caliphate during its conquest of Spain. While the Umayyads originated from Mecca, they fostered strong trade connections with Syria and played a prominent role in the Muslim conquest of Syria between 634-638 CE.
Traditionally, Palestinian thobes exhibit distinctive embroidery patterns that vary from one region to another. However, before exploring these patterns, it’s essential to understand the layering structure of these garments. The initial layer consists of an undergarment, often referred to by its Turkish term ‘gömlek
Gömlek: (Proto-Turkic: köyŋelek – Shirt; Azerbaijani: köynək – Shirt; Turkmen: koynek
Koynek: A traditional long, loose-fitting tunic or dress worn by Turkmen women in Central Asia typically made of silk or cotton, adorned with intricate embroidery, and often characterized by vibrant colours and geometric patterns. It is cultural symbol of significant importance reflecting the artistic heritage of Turkmen people. – long loose tunic dress), a traditional calf-length sleeved undershirt or tunic generally made of a plain white cotton, silk, or linen fabric, some more lightweight than others, worn by both Ottoman men and women of all communities throughout the empire. Irdān: (Arabic: ridān – sleeve), long triangular winged cuffed sleeves of a robe from the Levant Arb region, especially Palestine, Jordan, and Syria. The triangular cuffs were usually a decorative addition that were often tied at the back of the dress while doing regular chores. Qumbāz: (Arabic; Synonyms: sayah
Ṣāyah: (Classical Persian: sāya – shadow; Synonyms: zubūn, qumbāz, gombaz, yalak
Yalak: (Ottoman Turkic: yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. – a hip or waist length vest; from Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest), a short-sleeved waistcoat traditionally worn by men and a long outer robe or tight jacket either sleeveless or short sleeved with a tight bodice traditionally worn by women in the Ottoman controlled Levant. Yalak: (Ottoman Turkic: yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. – a hip or waist length vest; from Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest), a short-sleeved waistcoat traditionally worn by men and a long outer robe or tight jacket either sleeveless or short sleeved with a tight bodice traditionally worn by women in the Ottoman controlled Levant.
Nevertheless, costumes across Palestine exhibit significant variation from one region to another, in terms of their patterns, techniques of craftsmanship, and fabric choices. By acquiring comprehensive knowledge and insight through the study of costumes from each region, one can discern their origins based on their distinctive features.
Ramallah
Commencing with Ramallah and its nearby areas, the thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. commonly features white fabric for summer and black for winter. With its agreeable climate and picturesque vistas from its hilltops, Ramallah, meaning “Hill of God,” embodies a sense of blessing with its olive groves, fruit orchards, and fertile lands. With a flourishing community, Ramallah’s women hold a rich legacy of creative expression. They traditionally incorporated geometric designs in their embroidery, yet with the onset of Western influences in the early twentieth century, floral motifs emerged. These patterns adorned their headscarves and the renowned white Ramallah shawl Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . One distinctive motif is the rows of columns with pointed tops, symbolizing the ‘nakhla‘ or palm grove, embroidered in red over a white base.
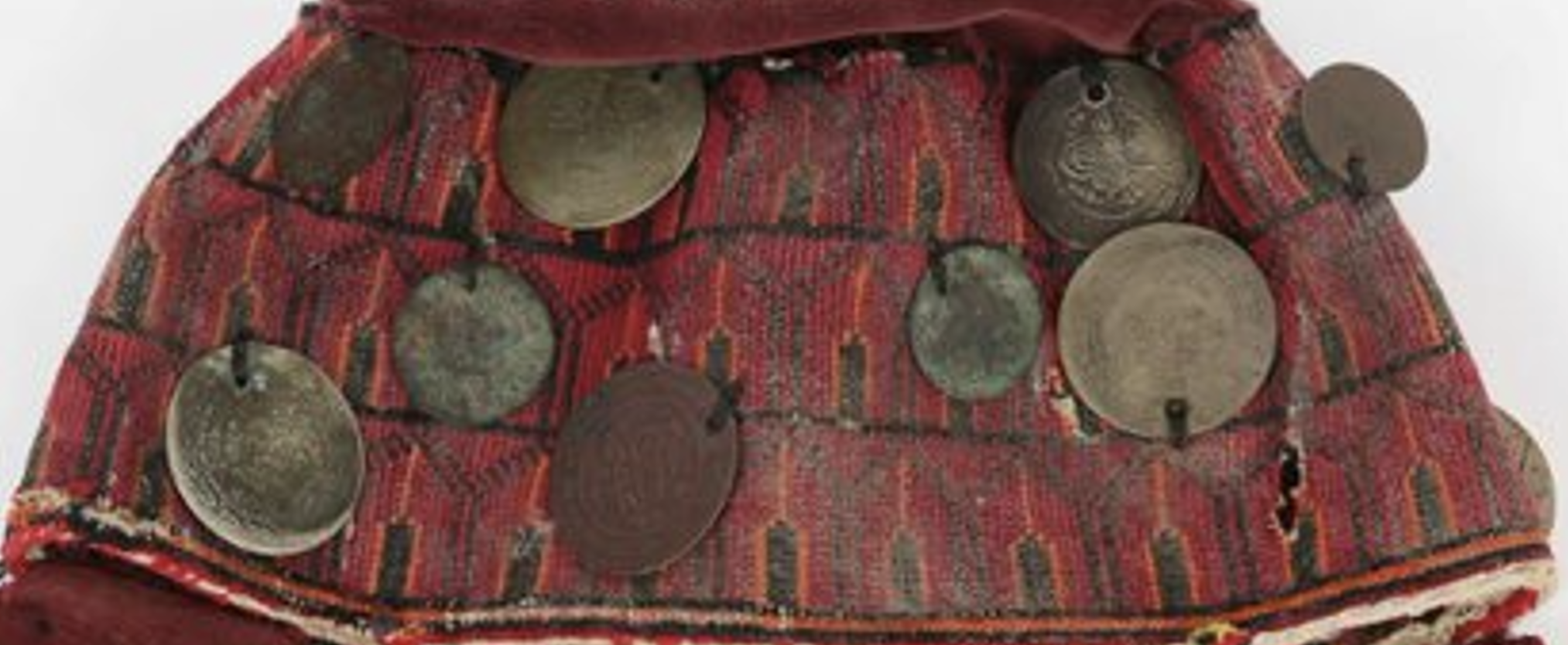

The famous ‘nakhla’ design of Ramallah on a cap from Hebron The Zay Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative collection.

Lower back panel of a Ramallah dress from Palestinian Embroidery – Widad Kawar.
Jerusalem
The hallmark characteristic of a Jerusalem dress lies in its fabric. These dresses are unmistakably recognized by either their striped silk fabric or their intricate tiled embroidered patterns. The striped silk fabric, known as ‘çitari,’in Ottoman Turkish was particularly favoured by the residents of Jerusalem and Bethlehem. During the Ottoman era, this fabric was frequently imported from Syria, where it was locally manufactured for the Arab community. While renowned throughout Syria since Ottoman times, in Palestine, it gained popularity among the inhabitants of Jerusalem and Bethlehem, possibly due to the region’s flourishing trade and affluent population.
Frequently, it was employed to craft ankle-length, front-open robes called ‘qumbaz
Qumbāz: (Arabic; Synonyms: sayah
Ṣāyah: (Classical Persian: sāya – shadow; Synonyms: zubūn, qumbāz, gombaz, yalak
Yalak: (Ottoman Turkic: yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. – a hip or waist length vest; from Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest), a short-sleeved waistcoat traditionally worn by men and a long outer robe or tight jacket either sleeveless or short sleeved with a tight bodice traditionally worn by women in the Ottoman controlled Levant. Yalak: (Ottoman Turkic: yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. – a hip or waist length vest; from Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest), a short-sleeved waistcoat traditionally worn by men and a long outer robe or tight jacket either sleeveless or short sleeved with a tight bodice traditionally worn by women in the Ottoman controlled Levant. Passementerie: (French: passement – braid), decorative trimmings or edgings for textile, often made of threads of silk, cotton, or precious metals such as gold and silver, generally braided or twisted into cords.
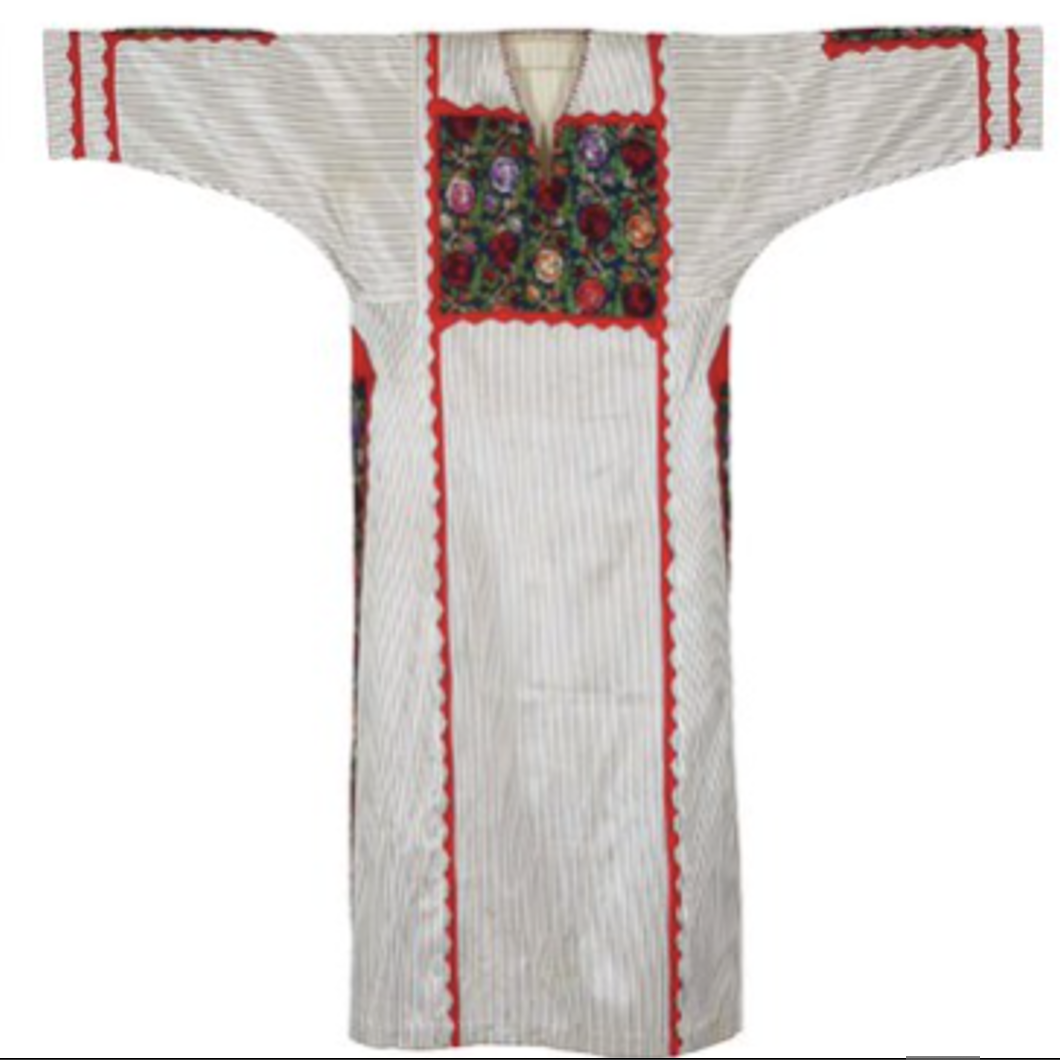

A striped silk dress from Jerusalem from The Zay Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative collection.
Yet another remarkably distinctive attribute of a Jerusalem dress is its prominent tiled patterns, particularly evident in the ‘qabbah
Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan)
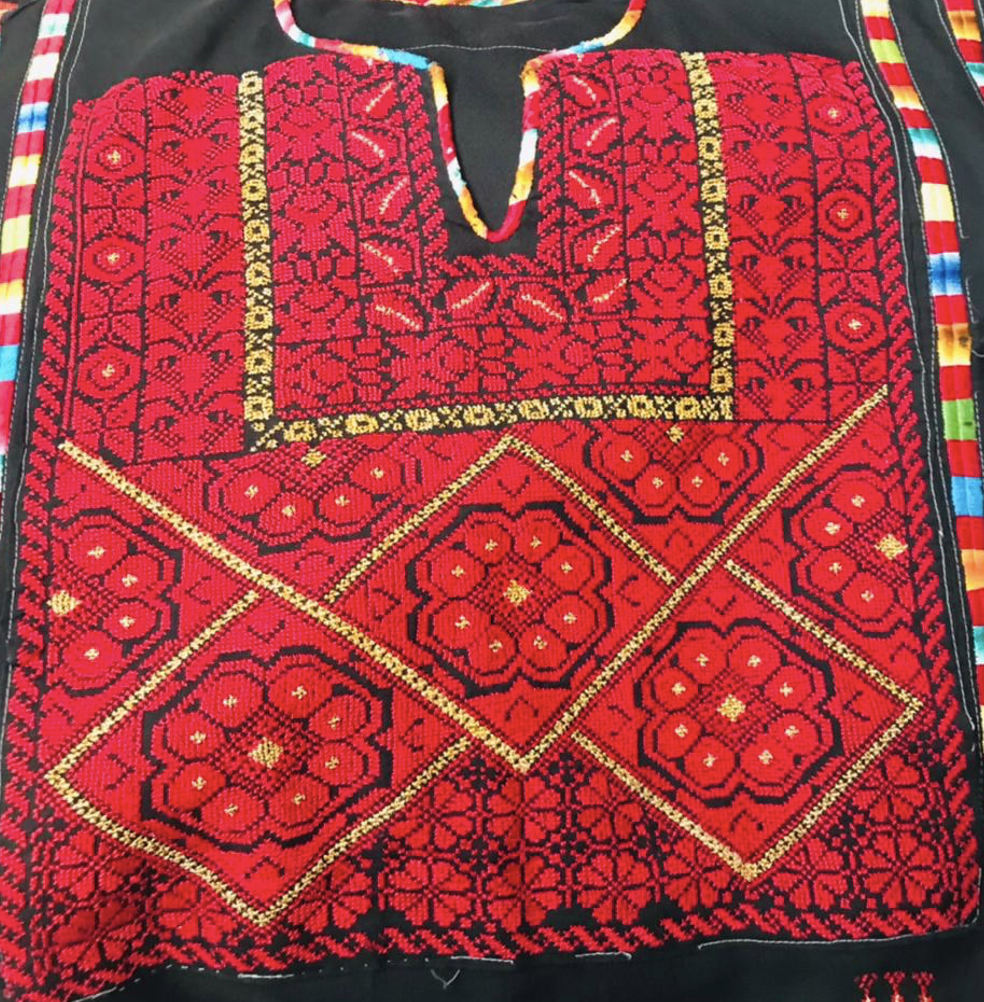

A ‘qabbah
Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan)
Bethlehem
The distinguishing trait of a Bethlehem thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. lies in its embroidery technique. Unlike other Palestinian thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. , which typically showcase cross-stitch patterns, garments from the Bethlehem region often display couching
Couching: (Latin: collocare – Place together), in needlework and embroidery couching is a technique in which yarn or other materials are laid across the surface of the ground fabric and fastened in place with small stitches of the same or a different yarn
Thobes from this region are distinguished by their curvilinear couching
Couching: (Latin: collocare – Place together), in needlework and embroidery couching is a technique in which yarn or other materials are laid across the surface of the ground fabric and fastened in place with small stitches of the same or a different yarn
The ‘thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. malek,’ as its name implies, signifies the king of robes or a royal robe. It represents a long, loose tunic-style traditional garment, often adorned with winged sleeves and distinguished by intricate embroidery on luxurious, high-quality fabric. Originating from the Bethlehem region, the ‘malek’ style swiftly became an essential inclusion in every woman’s trousseau across Palestine. Typically crafted from a blend of linen and silk, the ‘malek’ dress features red and black panels, accentuated with patches of vibrant orange and green silk. The centrepiece of the ‘malek’ ensemble is the ‘qabbah
Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan)
renowned for its elaborate tahriry Taḥrīry: (Arabic) couching embroidery technique developed in Bethlehem. Differs from the predominantly cross-stitch style of embroidery found in the rest of Palestine. patterns—a unique Bethlehem style characterized by the intricate use of silver, gold, and silk cords intricately twisted into floral and curvilinear motifs, further enhanced by herringbone stitching.
Interestingly, embroidered garments from the region especially Palestine, Jordan and southern Syria often reflect similar motifs with variations which is believed to have evolved from patterns that dates to pre-Judeo-Christian and Islamic society. For example, the four circles on the ‘qabbah
Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan)
Additionally, each of these circles is in the form of spiral that represents the ever-changing days, months, years and seasons. Motifs such as these could be seen scattered throughout the ancient Mediterranean and the Near Eastern settlements excavated in present day Romania, Malta, Italy, Türkiye, Egypt and Greece.
Another such example is the ‘saa’. With a circular centre and two long ends this pattern is believed to have evolved from the Eastern Mediterranean idols symbolizing a human body. Such figurines from the Anatolian region of present-day Türkiye dates to at least between the late Achaemenid – c. 550-330 BCE – and the Western Roman period – c. 215 BCE-476 CE.
It is also interesting to note that while in its usual size and dimension the pattern is termed as ‘saa’, but when the pattern appears in smaller dimension on the side panels of the skirt of a ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ’, it is termed as children ‘aulad’.
Furthermore, the symbolism of pomegranate too is an interesting aspect. The cultural significance of the fruit around the world is undeniable. However, in the Middle, Near East and the Mediterranean the significance of the pomegranate is steeped in tradition and faith and have both positive and negative connotations.
According to some scholars of the Abrahamic faith the expulsion of Adam and Eve may have been because of a pomegranate and not an apple just like the fall of Persephone that led her to Hades in Greek and Roman myths. Having said that, the pomegranate is also the promised fruit of Paradise both in Christianity and Islam, thus becoming both the promised as well as the forbidden fruit.
The red arils of the pomegranate have been used as a symbol to represent blood over centuries in many cultures, which led the ancient Persians to use it on their shields as signs for protection and later came to symbolise the blood of Christ and his suffering – Passion of Christ – by the Christians. A fairly drought resistant in nature, this fruit bearing plant can also be categorized as the Biblical ‘Tree of Life’.
However, its symbolic significance in the Near and the Middle East stretches far beyond the advent of monotheism. Just like in the Greek and Roman myths, the pomegranate has played an important role in the myths and legends of the pre monotheistic faiths in the region, the significance of which has been later adopted by the Judeo-Christian and Islamic faiths and beliefs. Even today it is a common symbol of fertility during wedding rituals amongst many cultures across the world especially in the Middle and Near East.
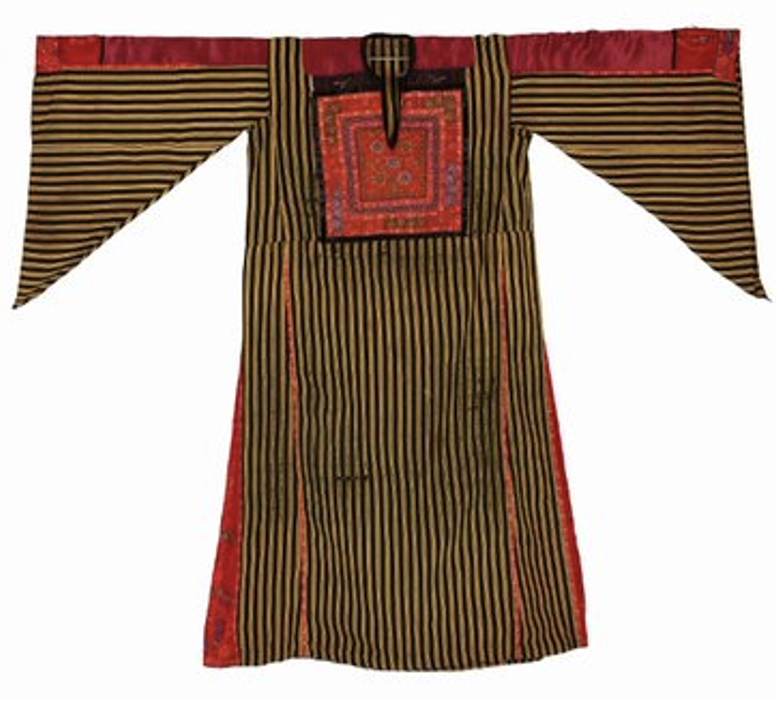

A Bethlehem ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ’ from The Zay Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative collection.
A Bethlehem dresses are traditionally paired with a ‘taksiri’ waistcioat, and the distinctive item holds a special place in Bethlehem’s fashion. A typical Bethlehem’ taksiri’ is a reminiscent of Ottoman ‘çepken’. Often made of velvet it features short half sleeves and a waist-length cut, and heavy couching
Couching: (Latin: collocare – Place together), in needlework and embroidery couching is a technique in which yarn or other materials are laid across the surface of the ground fabric and fastened in place with small stitches of the same or a different yarn
Gallilee
The typical attire of women from northern Palestine, especially from the Galilee regions, is distinguished by embroidered patterns adorning every piece of clothing, including trousers, jackets, and coats. Costumes from this area are notable for their utilization of various stitching techniques, influenced by the proximity to Syria and Turkey. A diverse array of embroidery methods, ranging from cross-stitch to satin
Sātin: (Arabic: Zaytuni: from Chinese port of Zayton in Quanzhou province where it was exported from and acquired by Arab merchants), one of the three basic types of woven fabric with a glossy top surface and a dull back. Originated in China and was fundamentally woven in silk. stitch, are employed in equal measure. Unlike the more intricate patterns found in central or southern Palestine, the designs in Galilee tend to be simpler. A recurring geometric motif prevalent in Galilee attire is the rhomboidal shape, symbolizing an amulet or ‘hujub
Ḥujub: (Arabic: plural of ḥijāb, amulets or protections), a traditional Levantine embroidery pattern resembling an amulet. Composed of a rhombus shape divided in four triangles by two perpendicular lines, topped with four small squares at the end. It is often embroidered using cross_stitch technique, mostly in the Jaffa surroundings in Palestine.
Hebron or Al Kahlil
The most identifiable characteristics of a Hebron ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ’ is its neckline and zigzag patterns on its chest panel. The patterns resembling a flight of stairs ‘daraj’ is although not unique to Hebron, however, their appearance in dresses from Hebron is far more frequent compared to other places. The ‘daraj’ is believed to be a derivative or interpretation of the crescent shape that is steeped in ancient Mesopotamian symbolism. It is believed that the crescent shape often associated with the moon is considered sacred because of the old Mesopotamian myth of Anat the moon goddess. Although with the passage of time changes in the cultural fabric of the region was noticed through the gradual decline of the ancient beliefs and the rise of monotheistic religions, however, the symbolism of the crescent shape remained with humanity.
The zigzag pattern is often considered an imagery of water and waves. In fact, the three point geometric shape also symbolises the rhythm of nature – birth, death, rebirth; morning, day and night; spring, autumn and winter.
However, the frequent appearance of these two patterns in costumes hailing from the Hebron area is also perhaps because of Hebron’s geography. Located in south of Jerusalem, the region features a hilly landscape with vineyards. It has been known for its rich and unique craftsmanship from glass and ceramics to leather and fabrics. Perhaps these design elements are reflections of the landscape that these highly skilled craftsmen community created centuries ago.
Opulently decorated dresses from Hebron were not only beautiful objects to wear on the day of the wedding, but also a way to demonstrate one’s skill and mastery of traditional techniques. Mastery of a discipline was paramount to proving one’s suitability as a bride. In the past, mothers looking for suitable brides for their sons would try to find the girl most skilled in embroidery. Their assumption was, if her embroidery was impeccable, she would make a perfect housekeeper and wife as well. It’s worth noting that the women residing in the city of Hebron did not typically wear the embroidered dress; rather, it was predominantly worn by those from the surrounding villages.
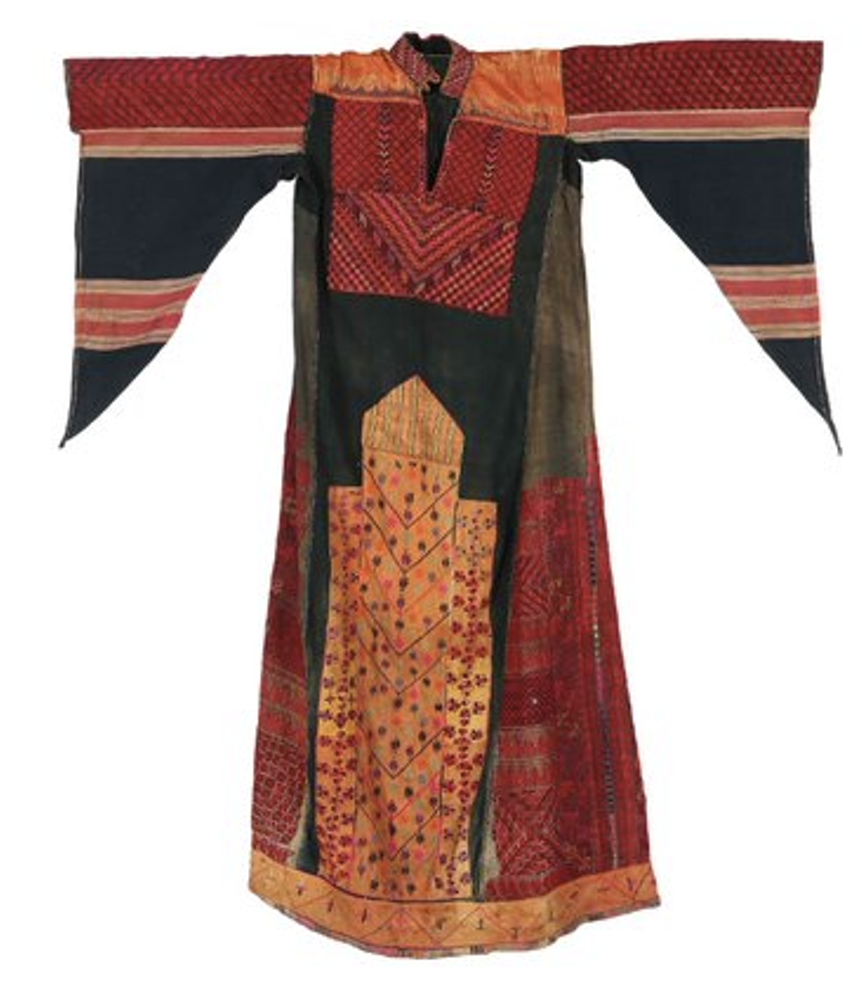
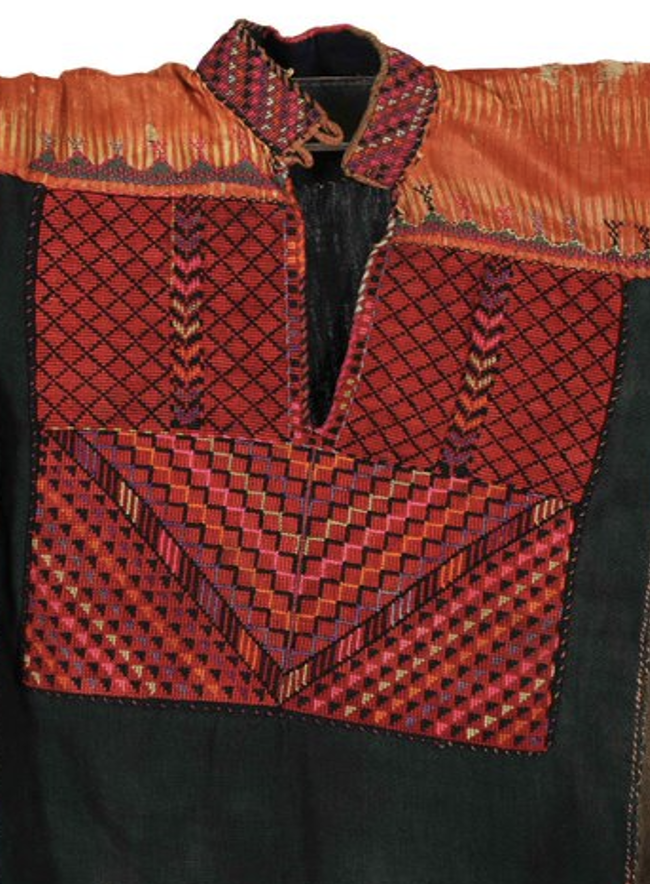


A Hebron ‘thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ’ and the closeup of its ‘qabbah
Qabbah: (Arabic) square chest piece made from a separate piece of fabric and added to the thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. in the countries of the Levant (Palestine, Syria, Jordan)
The Thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. Mekhmal
The ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. mekhmal’ is possibly the most prominent Ottoman influenced dress found in the Arab world. As the name suggests it is a ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. ’ made of velvet or ‘mekhmal’. The most opulently decorated ceremonial costume the ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. mekhmal’ is a dress styled after the Ottoman ‘bindali entari Entāri: (Turkish; Synonym: Antari), a traditional Turkish long jacket-like unisex garment worn during the Ottoman era. It often featured an open front with long sleeves and was worn over an undershirt and a pair of trousers and was sometimes layered by a short waist or hip-length jacket. .’ It is an ankle-length ceremonial overgarment characterised by a full skirt, small neckline, and straight full sleeves often made of dark-coloured velvet unique for its raised embroidered patterns depicting foliage and branches inspired by European Rococo art. During the last phase of the Ottoman Empire, the Ottoman society was gradually adopting such European inspired patterns which became popular across the Empire including the Levant.
Also known as ‘bilsarma’ these dresses featured Turkish dival Dīval: (Possibly Persian: divan – throne), an embroidery technique prominent during the Ottoman era done with metal threads or wire with a cardboard base usually over velvet. The motif is cut out on a cardboard and the metal thread is then embroidered over it using satin_stitch Satin_stitch: (Synonym: Damask Stitch), is a type of flat embroidery stitch that creates a satin like smooth and shiny surface by closely spaced stitches, covering an entire area or shape. and gimped couching style embroidery. embroidery in metal threads known as ‘sirma Sirma: (Byzantine Greek: súrma – a dragging motion, from Ancient Greek: súrō – to draw; Synonym: Tel_sirma Tel_sirma: (Ottoman Turkish: tel – wire, thread, chord; Byzantine Greek: súrma – a dragging motion from Ancient Greek: súrō – to draw; Synonym: Sirma), a metal lace or thread traditionally made of silver or gold and sometimes even copper often used textile embellishments such as embroidery and weaves like brocades. ), a metal lace or thread traditionally made of silver or gold and sometimes even copper often used textile embellishments such as embroidery and weaves like brocades. ’ in Ottoman Turkish. It comprised of satin Sātin: (Arabic: Zaytuni: from Chinese port of Zayton in Quanzhou province where it was exported from and acquired by Arab merchants), one of the three basic types of woven fabric with a glossy top surface and a dull back. Originated in China and was fundamentally woven in silk. stitch embroidery with metal threads often gold or silver that were passed over a leather or cardboard base to give it a relief or three-dimensional effect.
It is interesting to note how in the Arab world this technique of embroidery is often referred to as ‘sarma Ṣarma: (colloquially). Perhaps the word comes from the verb “sarama” meaning the piece of rope. Sarma: a kind of dense embroidery that is done with golden or silver threads in a way that completely covers the fabric, adding to it luxury and splendor. The embroidery is often three-dimensional, with a cotton padding wrapped in golden threads to create the height to the overall shape of the embroidery. Historically, Damascus was famous for it. It is believed that its origin is from India, and its name there is Sharma, then it moved to many countries, including Turkey, and its name there is Sirma Sirma: (Byzantine Greek: súrma – a dragging motion, from Ancient Greek: súrō – to draw; Synonym: Tel_sirma Tel_sirma: (Ottoman Turkish: tel – wire, thread, chord; Byzantine Greek: súrma – a dragging motion from Ancient Greek: súrō – to draw; Synonym: Sirma), a metal lace or thread traditionally made of silver or gold and sometimes even copper often used textile embellishments such as embroidery and weaves like brocades. ), a metal lace or thread traditionally made of silver or gold and sometimes even copper often used textile embellishments such as embroidery and weaves like brocades. , while in Algeria the name is Majboud.’ which is a derivative of the Turkish term for the material – metal threads or ‘sirma Sirma: (Byzantine Greek: súrma – a dragging motion, from Ancient Greek: súrō – to draw; Synonym: Tel_sirma Tel_sirma: (Ottoman Turkish: tel – wire, thread, chord; Byzantine Greek: súrma – a dragging motion from Ancient Greek: súrō – to draw; Synonym: Sirma), a metal lace or thread traditionally made of silver or gold and sometimes even copper often used textile embellishments such as embroidery and weaves like brocades. ), a metal lace or thread traditionally made of silver or gold and sometimes even copper often used textile embellishments such as embroidery and weaves like brocades. ’, while the Turkish term for the same technique ‘dival Dīval: (Possibly Persian: divan – throne), an embroidery technique prominent during the Ottoman era done with metal threads or wire with a cardboard base usually over velvet. The motif is cut out on a cardboard and the metal thread is then embroidered over it using satin_stitch Satin_stitch: (Synonym: Damask Stitch), is a type of flat embroidery stitch that creates a satin like smooth and shiny surface by closely spaced stitches, covering an entire area or shape. and gimped couching style embroidery.’ is thought to have originated from the Persian word for throne or council chamber – ‘divan’ – which was synonymously used for the lushly embroidered fabric used for its upholstery.
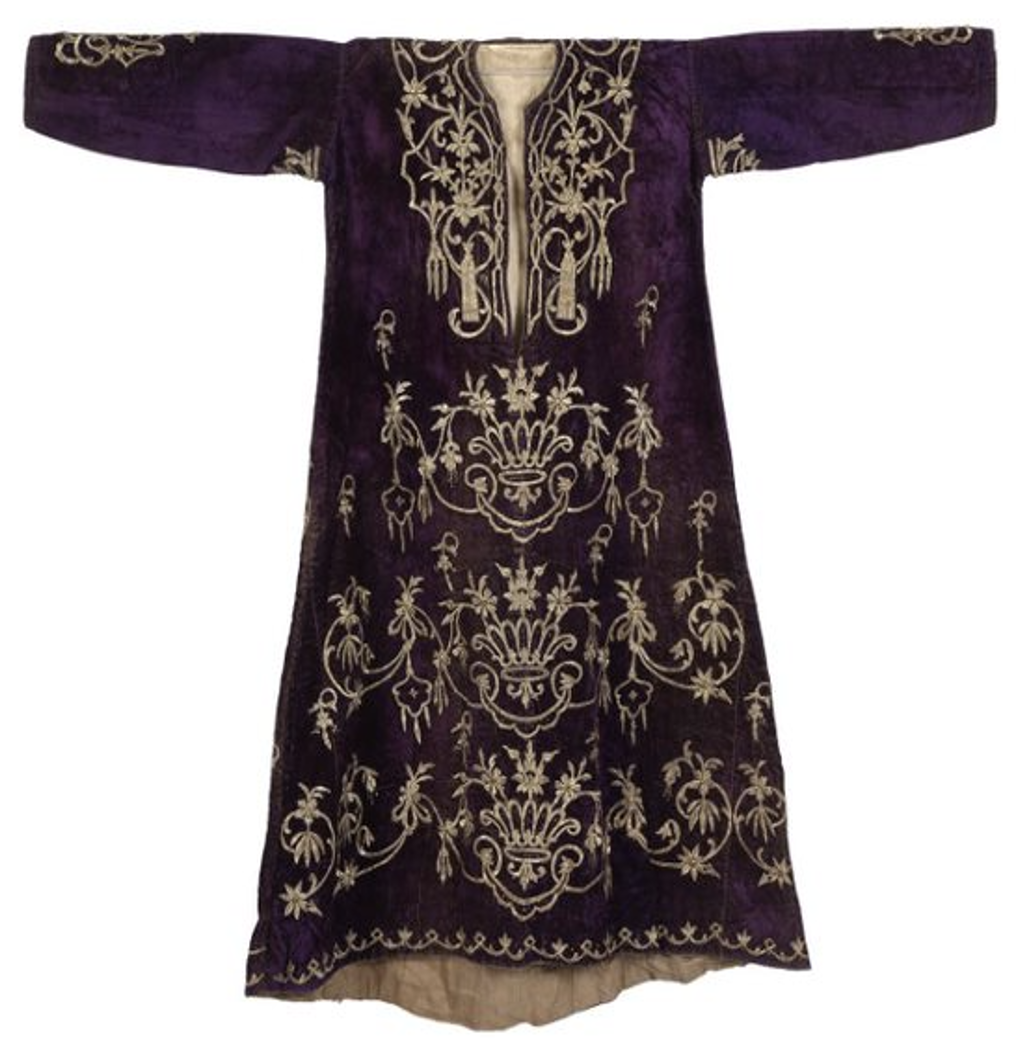

A ‘thobe Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. mekhmal’ from The Zay Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative collection.
In addition to the previously mentioned dresses and their distinctive techniques and patterns, which have evolved since ancient times, the recent history of traditional embroidery of the region is equally breath taking. During the 19th century, Christian missionaries from Europe and North America to the region opened schools for instructing and promoting the western form of Christianity that was deeply rooted in Roman Catholicism, post Reformation Protestantism, Anglican, Methodist and several other denominations. Embroidery and lacemaking were an integral part of this kind of education.
The textile skills learned and developed at these schools blended traditional Palestinian forms of embroidery with European techniques thus giving rise to a fabric that featured cross stitch and couching
Couching: (Latin: collocare – Place together), in needlework and embroidery couching is a technique in which yarn or other materials are laid across the surface of the ground fabric and fastened in place with small stitches of the same or a different yarn
However, the dress and embroidery traditions of the early 20th century saw a radical decline after the late 1940s. The creation of the State of Israel and war in the 1960s contributed to the disuse of hand embroidered textiles with very few women having the time or money to continue supporting and contributing to the embroidery industry.
Indeed, the pace of decline and loss of knowledge concerning the craft, as well as the traditional styles and designs, is accelerating due to the ongoing conflict. As a result, it is increasingly challenging to document and preserve this heritage for the benefit of future generations.
In conclusion, although various non-profit organizations are striving to conserve Palestinian heritage, the endeavour to do so uniformly across all aspects of cultural heritage demands substantial efforts.