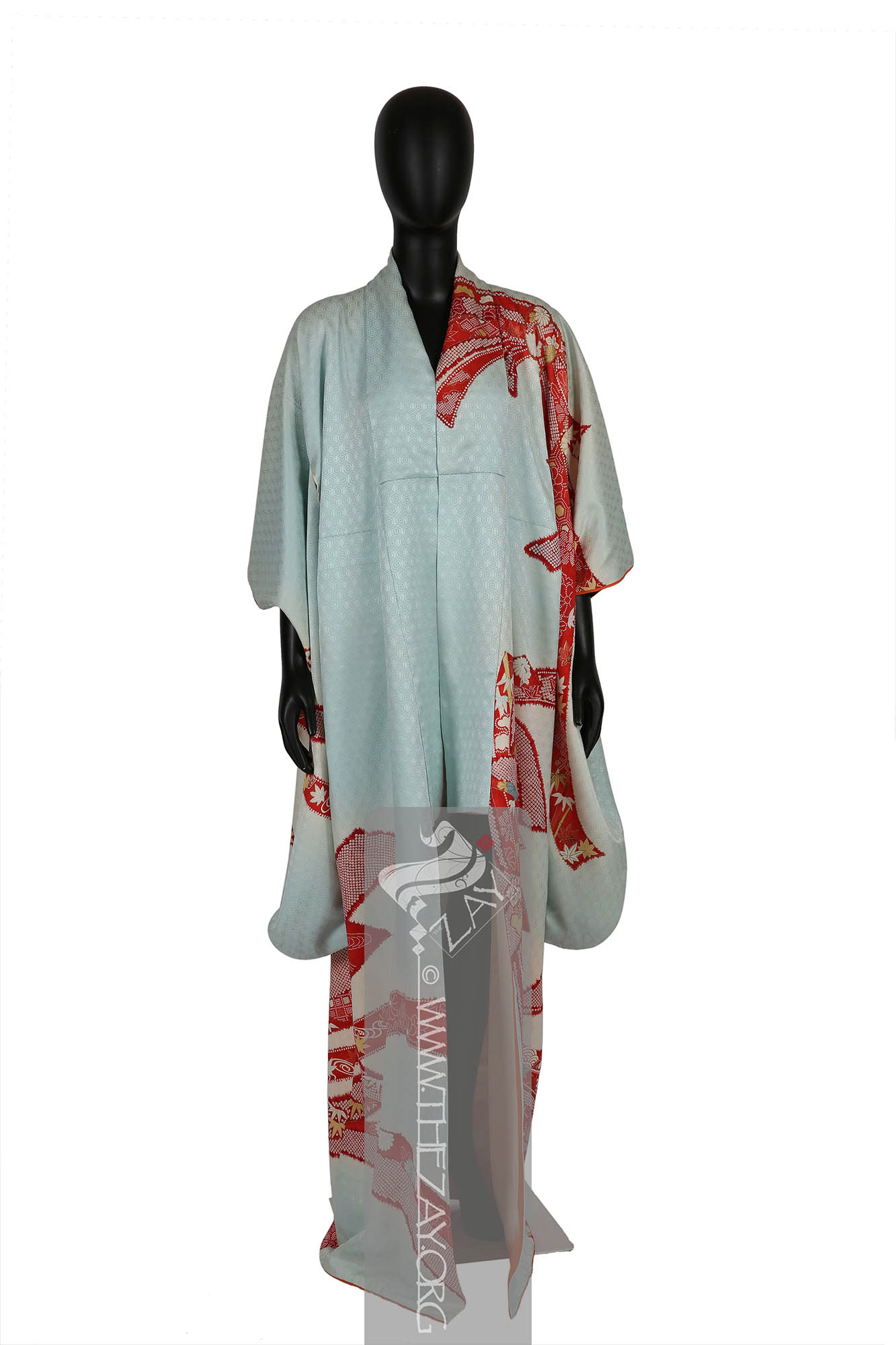
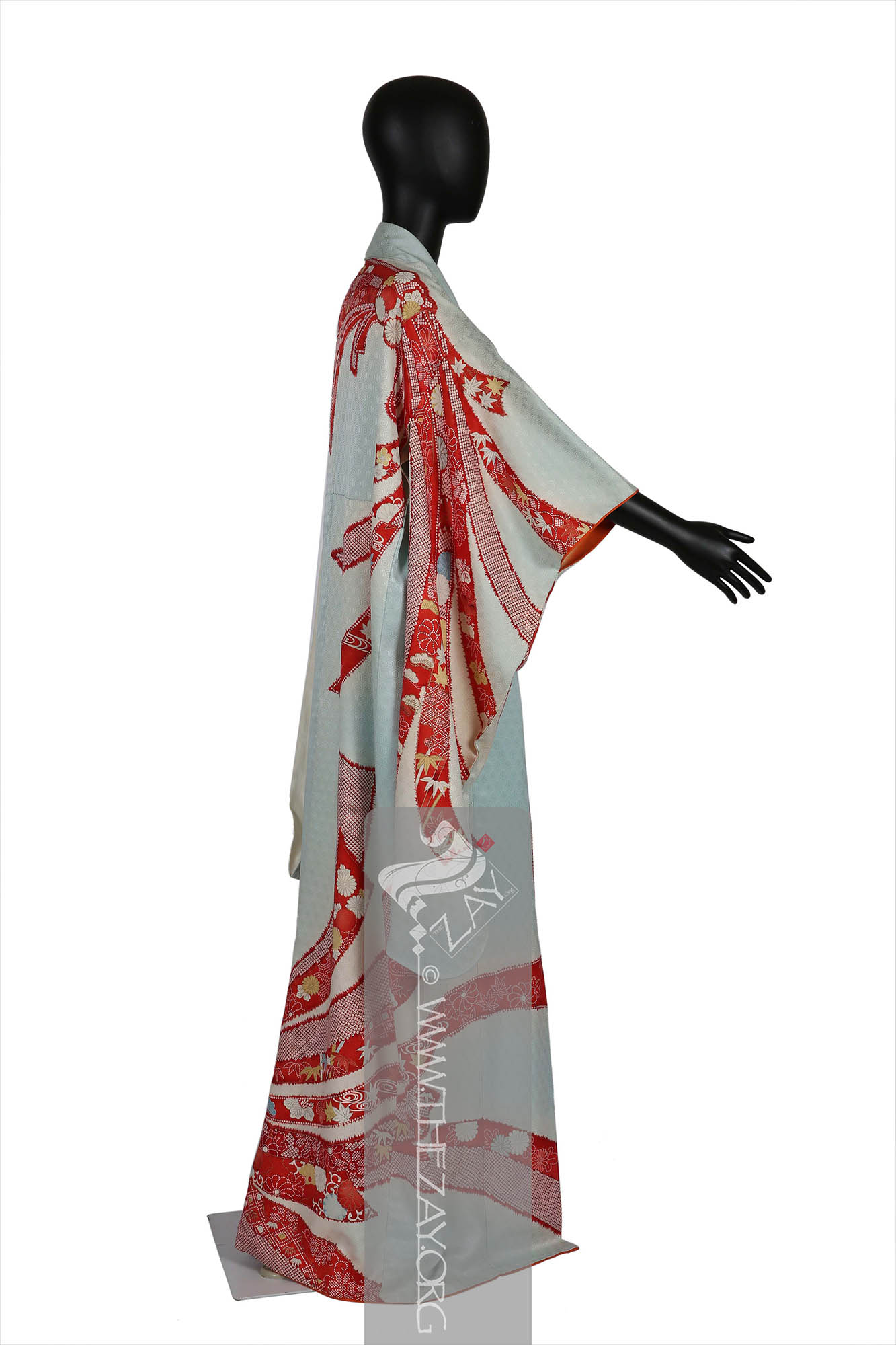
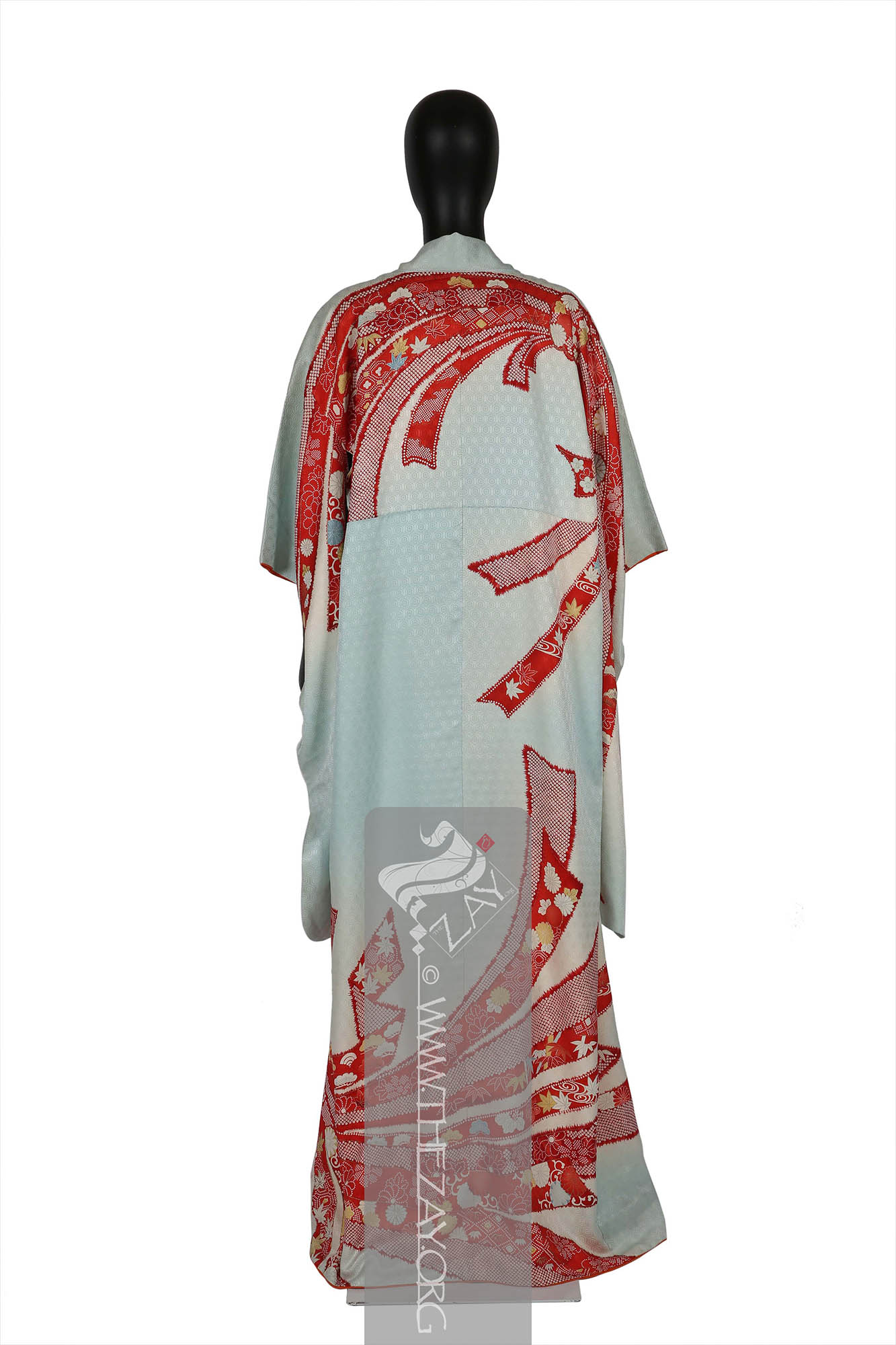
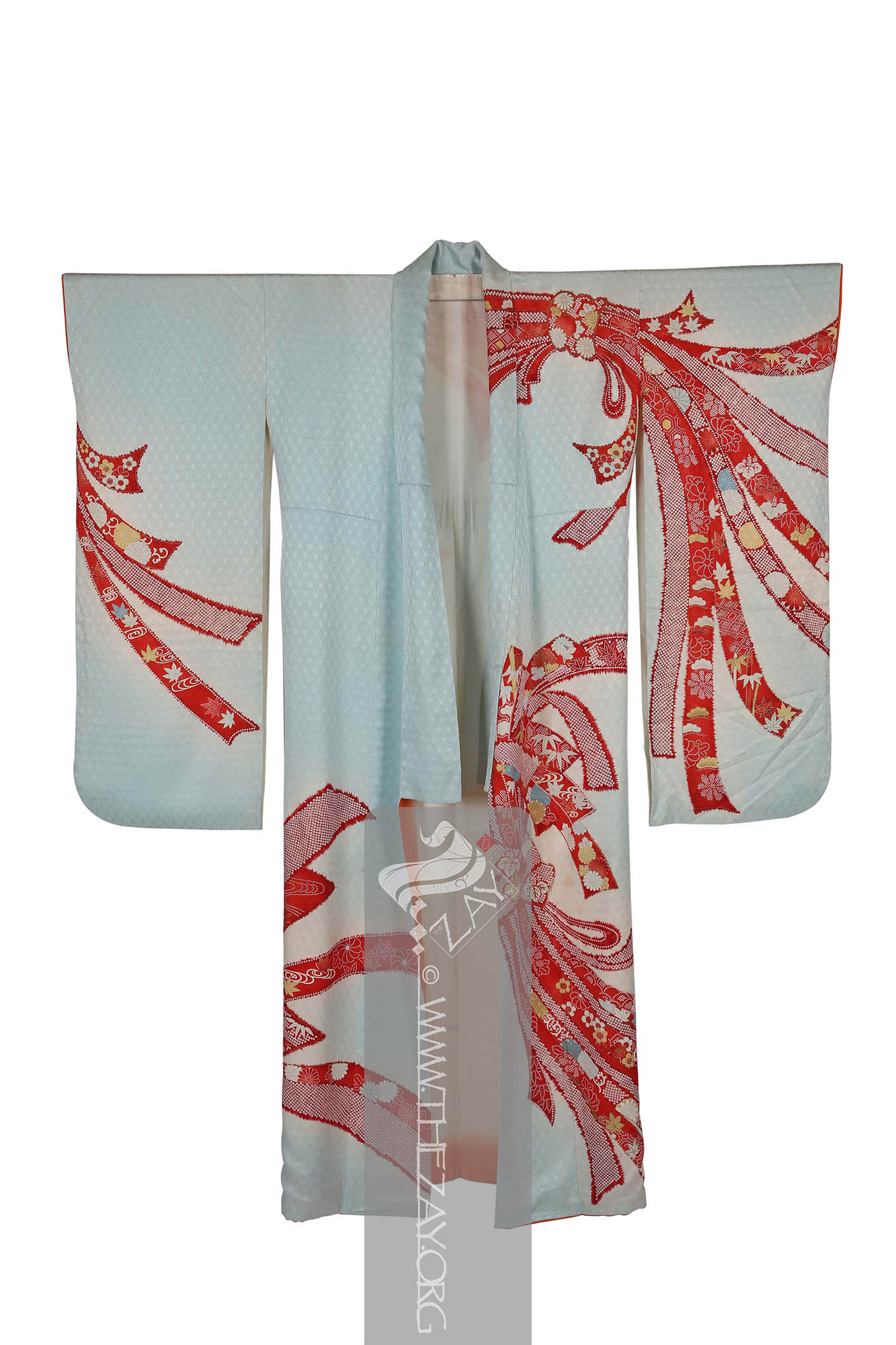
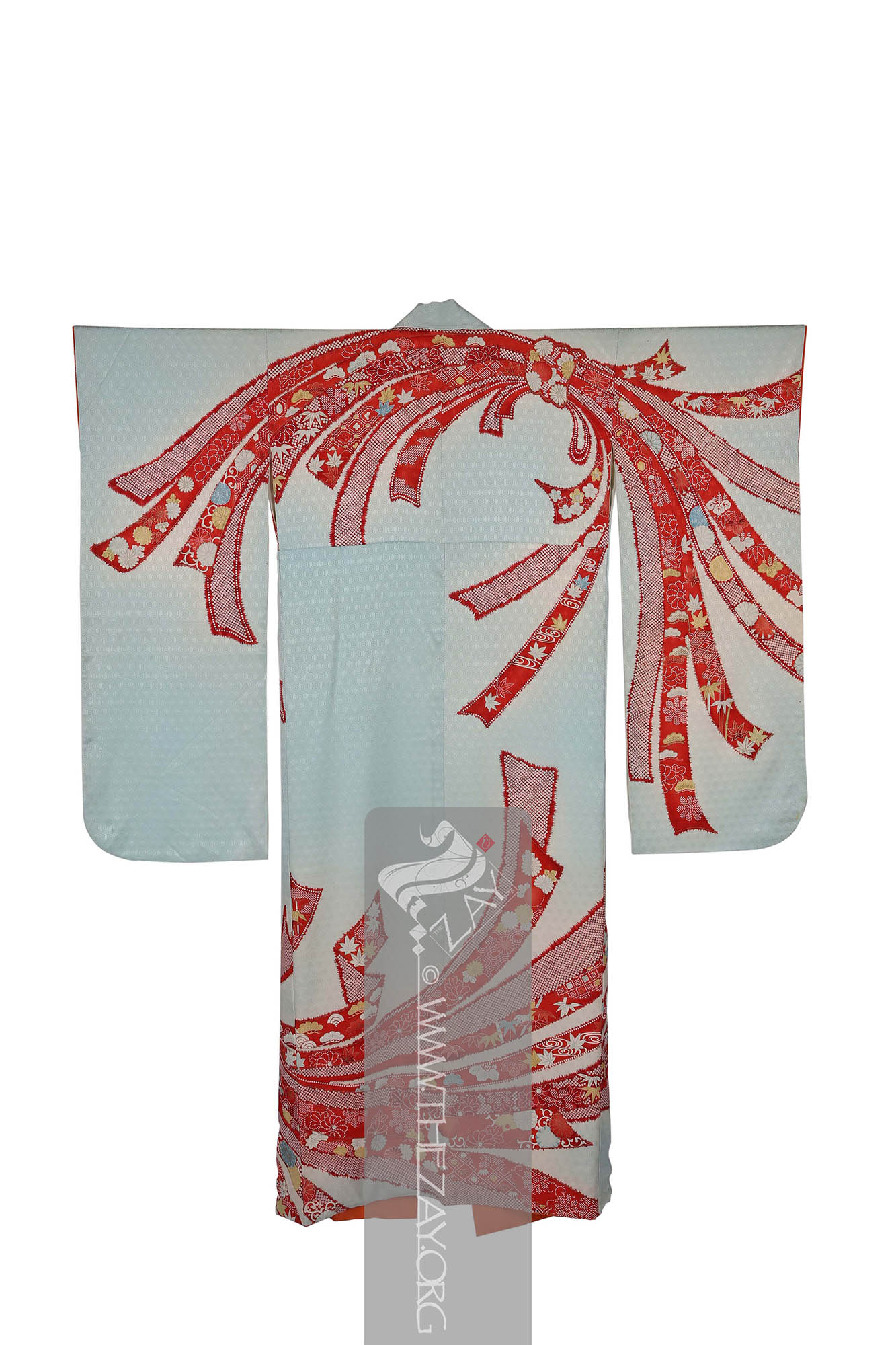
Object History This beautiful light blue and ivory (
furisode_kimono
Furisode_kimono: (Japanese: Furisode – swinging sleeves), a type of kimono characterised by its long sleeves that can reach up to the ankles. Traditionally worn by only unmarried women for formal events. It often features a vibrant design that covers the entire fabric and is typically made of silk. ) was purchased by
Dr. Reem Tariq
Ṭariq: (Arabic; Synonym: tulle_bi_talli; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the Levant Arab region specifically in Lebanon.
El Mutwalli
Dr. Reem Tariq
Ṭariq: (Arabic; Synonym: tulle_bi_talli; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the Levant Arab region specifically in Lebanon.
el Mutwallī: Founder (CEO) of the Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative, a public figure, speaker and author. An expert curator and consultant in Islamic art and architecture, interior design, historic costume, and UAE heritage. in 2017 from a dealer in Japan, to be added to The
Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative collection.
Object Features This is blue and ivory (rinzu
Rinzu: A type of silk damask textile that is characterised by its smooth and glossy surface, intricate patterns, and subtle use of colour. Both dyed and undyed threads are combined to produce a shiny or subtle repeat pattern over a matte surface enriching the depth of the textile. ) or damask
Dāmāsk: (Arabic: Damascus – a city in Syria), is a luxurious fabric woven with reversible patterns typically in silk, wool, linen, or cotton. Originating in China, the fabric was perhaps introduced to European traders at Damascus – a major trading post on the Silk Road with a thriving local silk industry. (chirimen
chirimen: A Japanese crepe
Crepe: (Latin: crispus; Old French: crespe – curled or frizzed), is a lightweight, crinkled fabric with a pebbled texture woven from a hand spun untreated or ‘in the gum’ silk yarn.
fabric traditionally made from silk. It has a distinctive pebbly texture and is commonly used in kimono and other traditional garments. Originally brought from China chirimen weaving extensively developed during the Edo period (1603-1868) and continues to be a popular textile in modern Japan. ) silk woman’s kimono
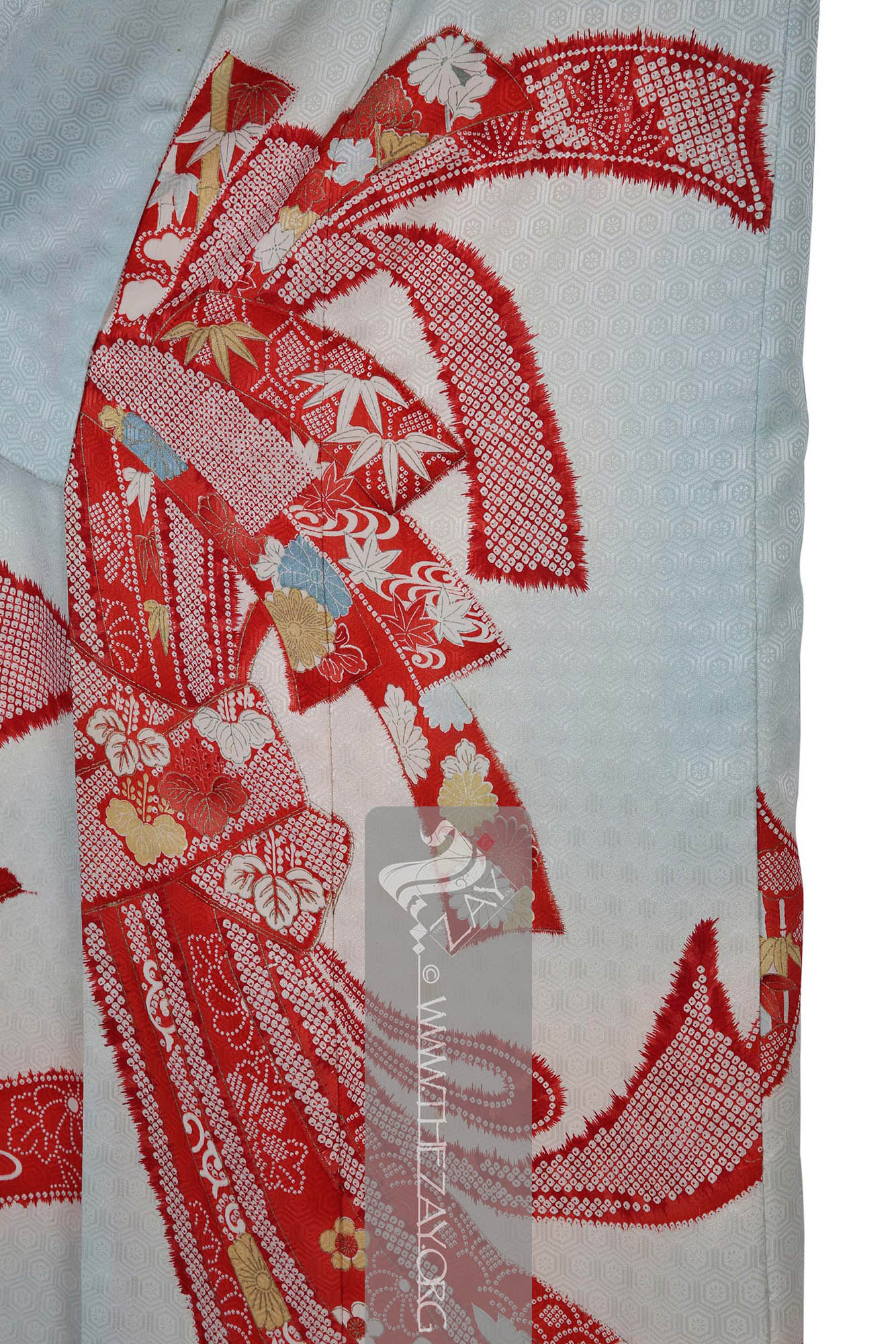
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. embellished with printed designs in shades of red, yellow and ivory with green and gold highlights. It has long sleeves with triple openings and a metal snap button on the neck to possibly to keep it folded and secure it away from the neck while wearing making it a woman’s furisode kimono
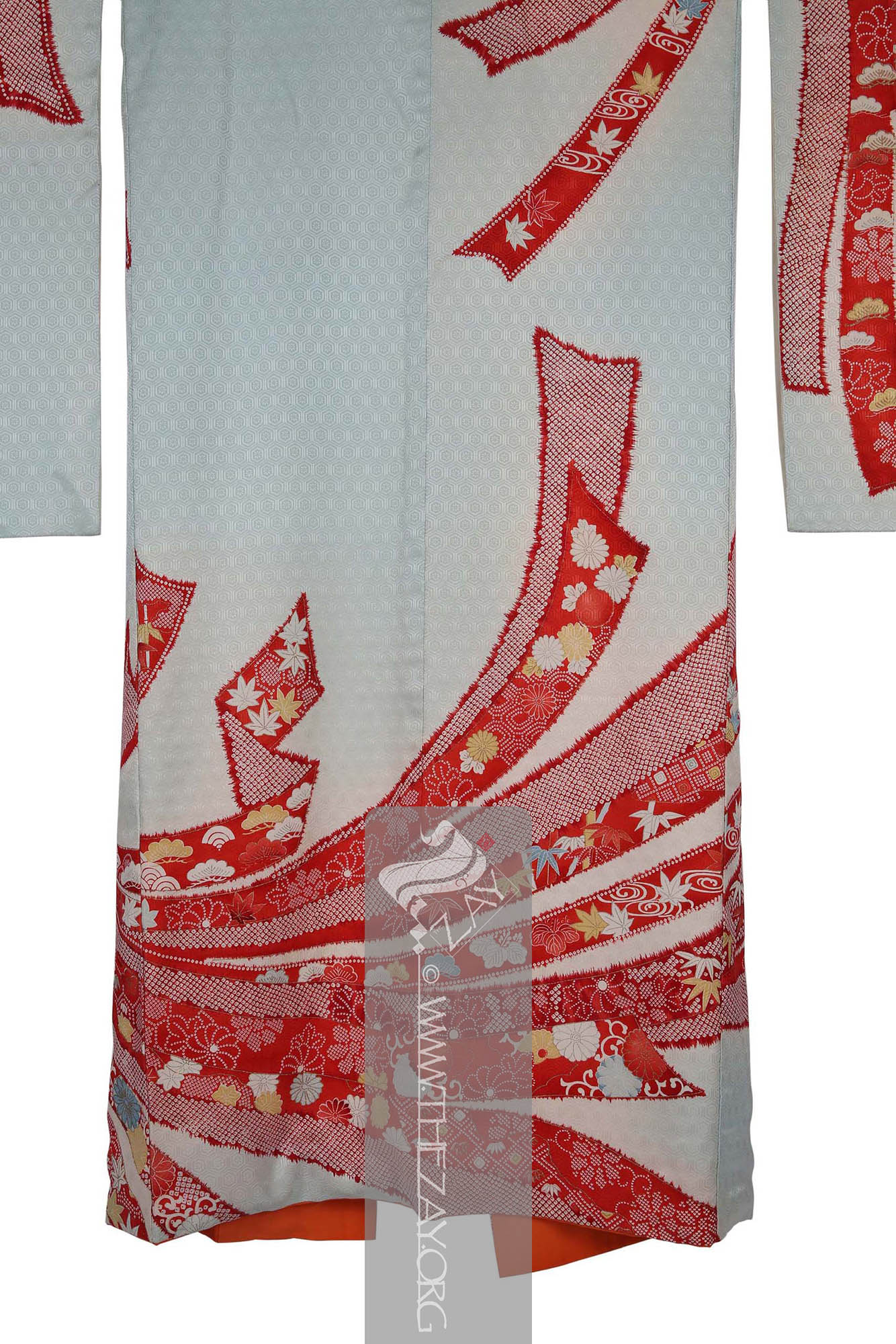
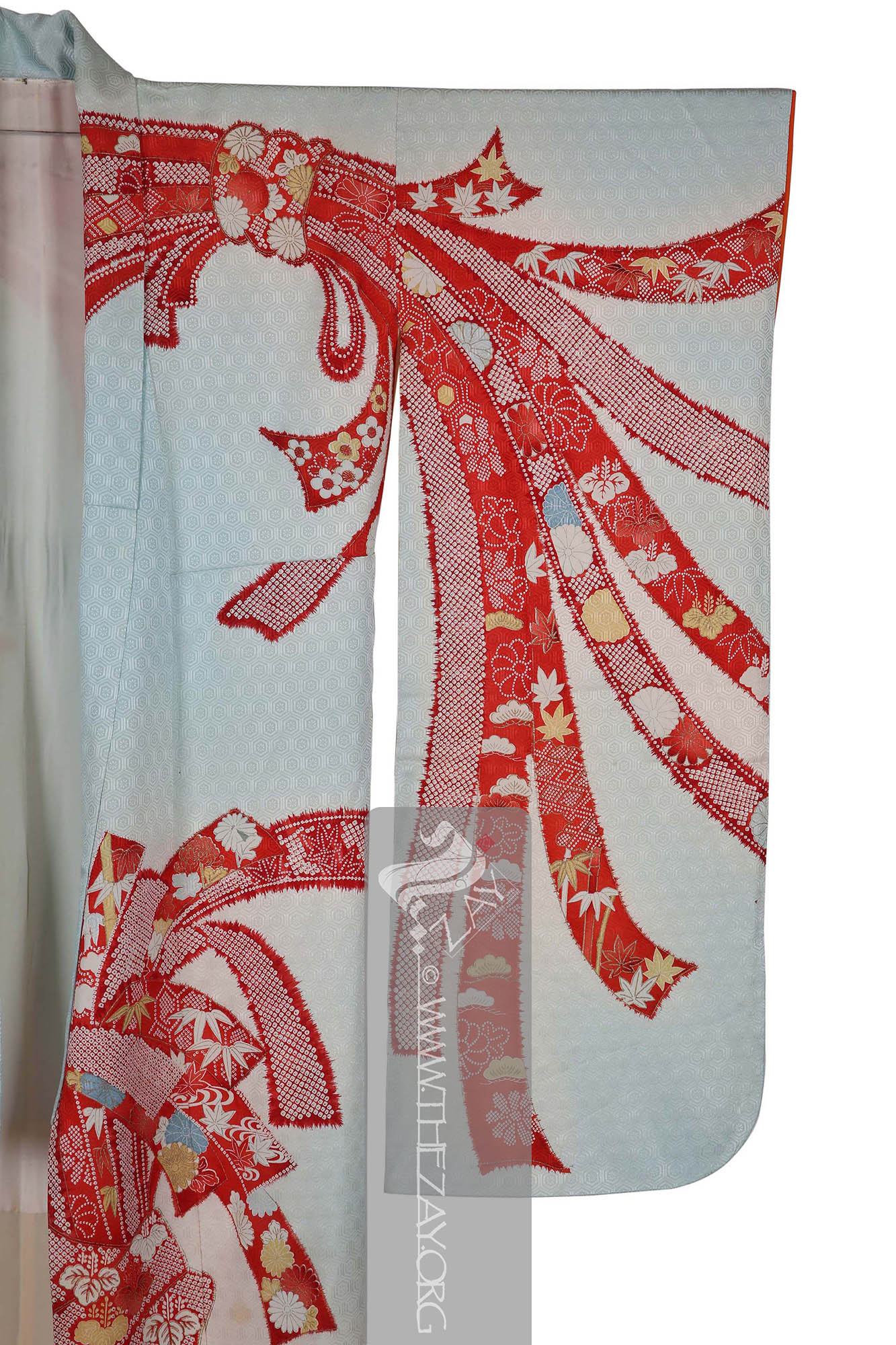
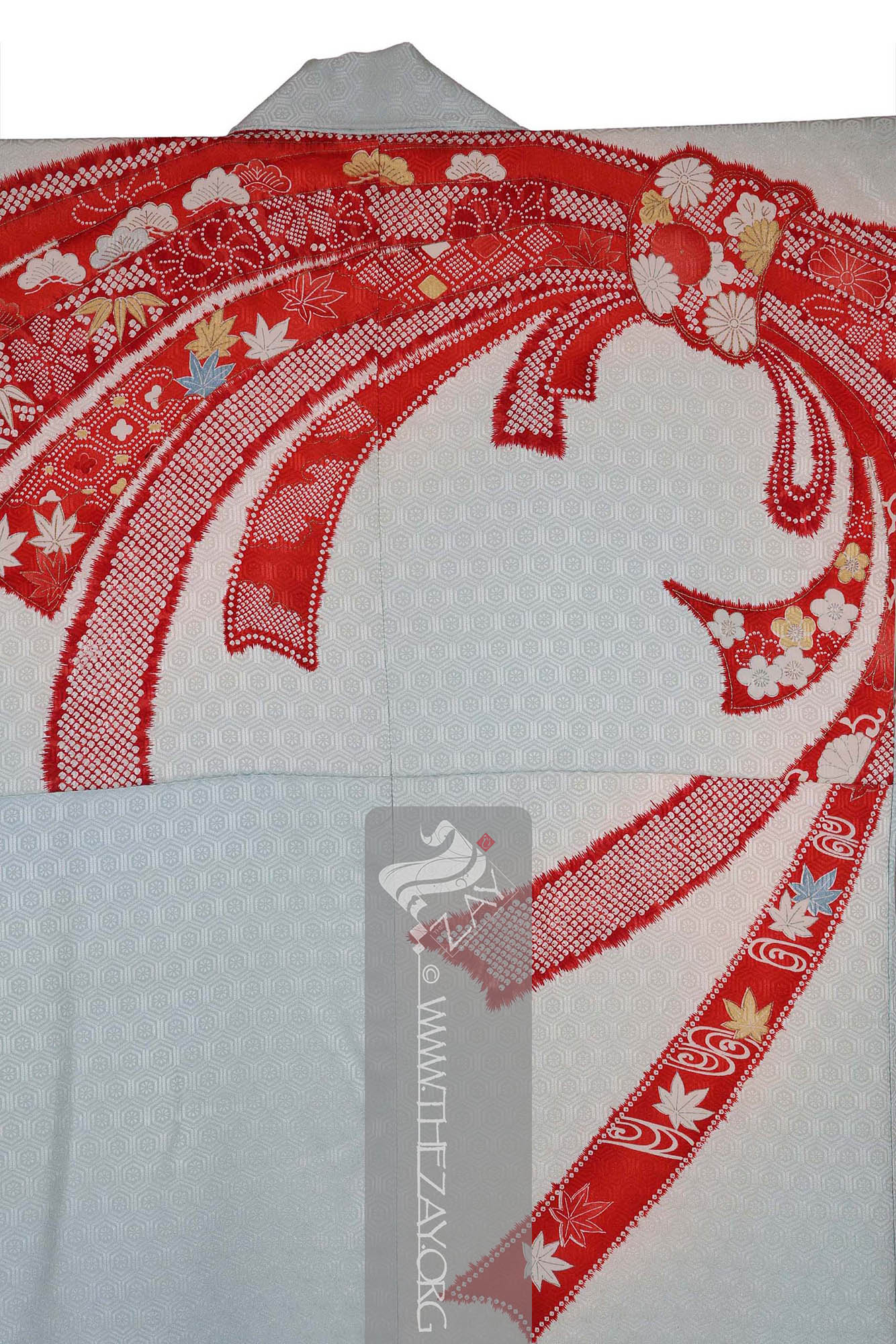
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. . Large (yuzen_printed) auspicious strips of dried fish and seaweed bundle – noshi – motifs primarily in shades of red, yellow and blue and gold foils curl themselves around the
furisode_kimono
Furisode_kimono: (Japanese: Furisode – swinging sleeves), a type of kimono characterised by its long sleeves that can reach up to the ankles. Traditionally worn by only unmarried women for formal events. It often features a vibrant design that covers the entire fabric and is typically made of silk. .
The
rinzu
Rinzu: A type of silk damask textile that is characterised by its smooth and glossy surface, intricate patterns, and subtle use of colour. Both dyed and undyed threads are combined to produce a shiny or subtle repeat pattern over a matte surface enriching the depth of the textile. damask
Dāmāsk: (Arabic: Damascus – a city in Syria), is a luxurious fabric woven with reversible patterns typically in silk, wool, linen, or cotton. Originating in China, the fabric was perhaps introduced to European traders at Damascus – a major trading post on the Silk Road with a thriving local silk industry. pattern is in the form of little hexagon repeats all over the field creating an additional layer of design on it. Patches within the noshi bundles are decorated in (
shibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. ) dyed techniques.
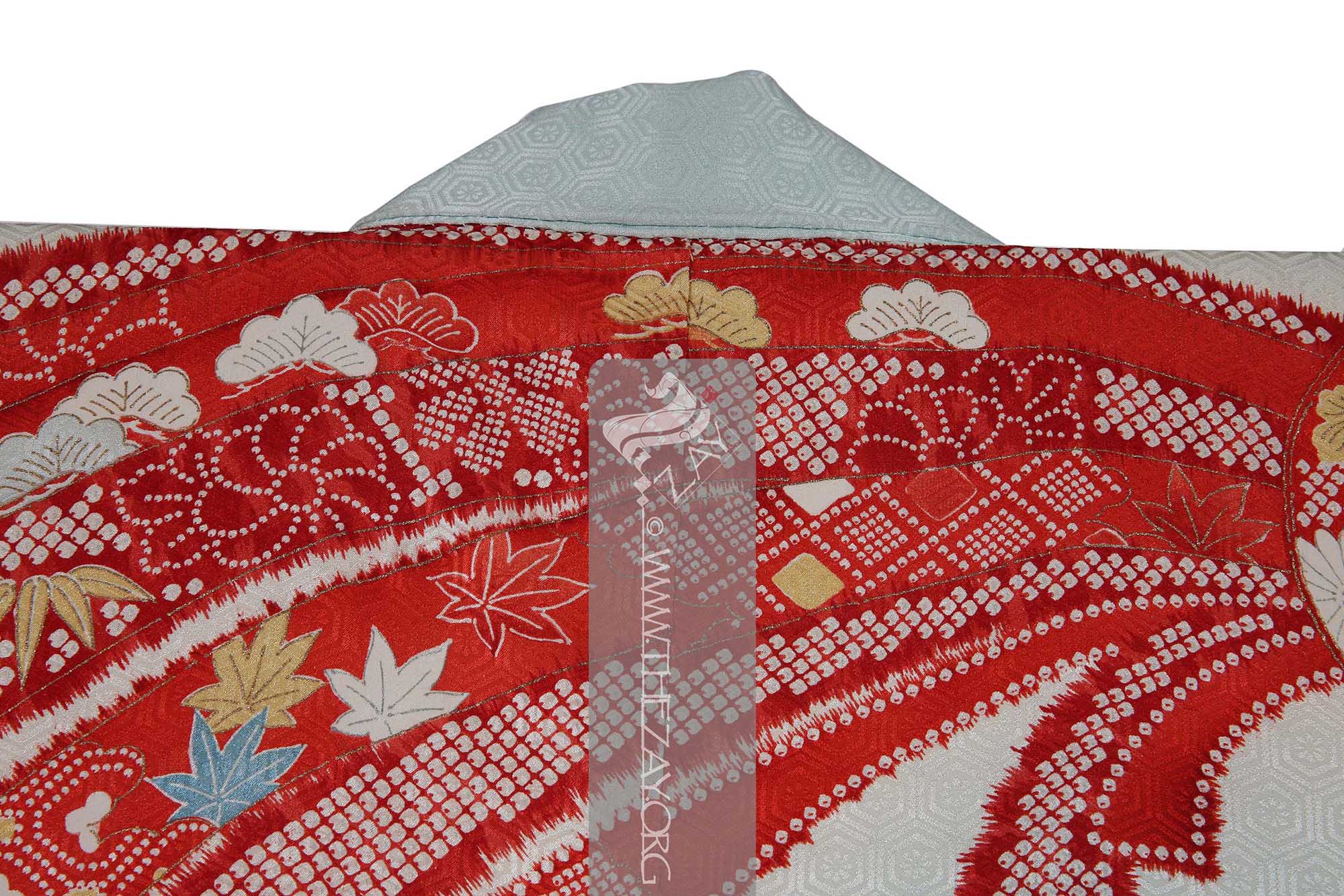
There are additional design elements within the noshi bundles such as the holy trinity of Japanese auspicious motifs the pine tree – sho – bamboo – chiko – and plum – bai – executed in (
katazome_print
Katazome_print: A traditional Japanese resist printing technique where a stencil is used to apply a rice paste resist onto fabric before dyeing, creating intricate and precise patterns. First developed as a substitute to expensive and time-consuming woven brocade it became a well-respected fabric art over time. ) that adds another layer to this furisode. Parts of the design has been highlighted with pressed gold leaf – kinpaku – giving it a very rich look.
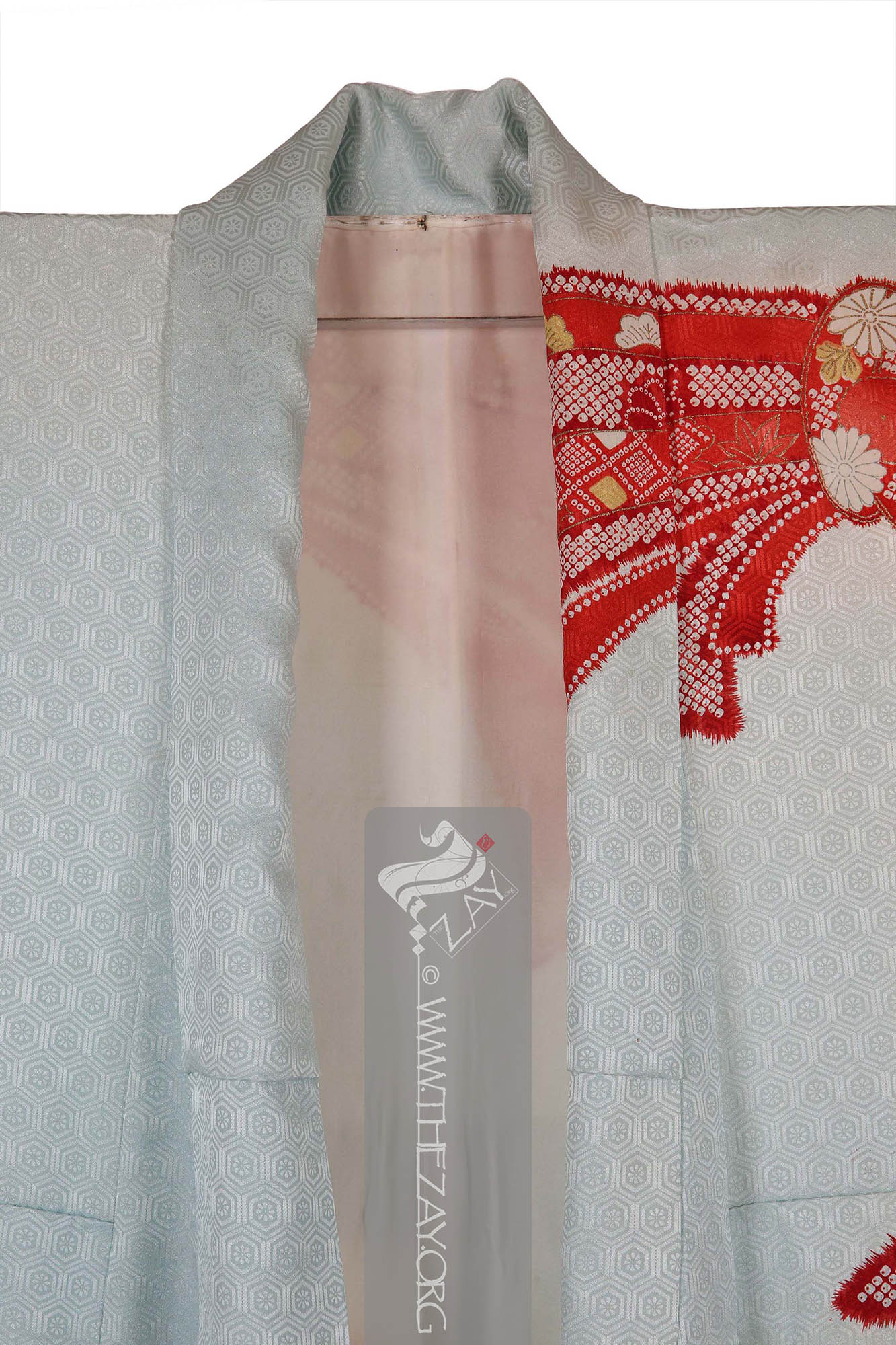
The lining of the piece is a plain ivory
chirimen
chirimen: A Japanese crepe
Crepe: (Latin: crispus; Old French: crespe – curled or frizzed), is a lightweight, crinkled fabric with a pebbled texture woven from a hand spun untreated or ‘in the gum’ silk yarn.
fabric traditionally made from silk. It has a distinctive pebbly texture and is commonly used in kimono and other traditional garments. Originally brought from China chirimen weaving extensively developed during the Edo period (1603-1868) and continues to be a popular textile in modern Japan. with the edges near the hems of the sleeves as well as the fall
shibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. dyed in a bright shade of orange gradient.
It is interesting to note that from the early Edo period – 1603-1868 –
furisode_kimono
Furisode_kimono: (Japanese: Furisode – swinging sleeves), a type of kimono characterised by its long sleeves that can reach up to the ankles. Traditionally worn by only unmarried women for formal events. It often features a vibrant design that covers the entire fabric and is typically made of silk. characterized by their long sleeves had become the standard formal wear for unmarried women. The use of multi layered auspicious symbolisms like the seaweed or noshi bundles along with the pine tree – sho – bamboo – chiko – and plum – bai – in this piece suggests that this
furisode_kimono
Furisode_kimono: (Japanese: Furisode – swinging sleeves), a type of kimono characterised by its long sleeves that can reach up to the ankles. Traditionally worn by only unmarried women for formal events. It often features a vibrant design that covers the entire fabric and is typically made of silk. was perhaps made for an unmarried woman’s coming of age ceremony.
While the origin of certain techniques and methods in textiles like
satin_stitch
Satin_stitch: (Synonym: Damask Stitch), is a type of flat embroidery stitch that creates a satin like smooth and shiny surface by closely spaced stitches, covering an entire area or shape. embroidery can be traced to China, and its spread across the world could be attributed to the Silk Road, other similar techniques and styles are believed to have originated independently in different regions of the world almost simultaneously in human history possibly from necessity and convenience.
Though The
Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative is concerned mainly with the dress and adornment heritage of the Arab world, it does include in its collection articles from areas outside the region. These tend to be collected to illustrate specific shared elements and influences attesting that the Arab world never existed in a vacuum. It constantly drew, and continues to draw, inspiration and influences from the cultures it comes in contact with be it through trade or geopolitical circumstances, especially those countries within the old silk route.
Therefore, one cannot but draw parallels between many techniques used in such garments, such as (
couching
Couching: (Latin: collocare – Place together), in needlework and embroidery couching is a technique in which yarn or other materials are laid across the surface of the ground fabric and fastened in place with small stitches of the same or a different yarn
) and thread knotting techniques (
macrame
Macrame: (French: macramé – A hand-knotted textile from Turkish: makrama – table spread or towel, from Arabic: miqrama – bedspread possibly with knotted hanging fringes resembling dangling grapes or karam in Arabic) A form of textile or fringe made by a knotting cord in geometrical patterns possibly originating in Babylon and Assyria.Macrame
Macrame: (French: macramé – A hand-knotted textile from Turkish: makrama – table spread or towel, from Arabic: miqrama – bedspread possibly with knotted hanging fringes resembling dangling grapes or karam in Arabic) A form of textile or fringe made by a knotting cord in geometrical patterns possibly originating in Babylon and Assyria.: makrəˌmā: (Arabic: karam: tree with dangling grapes), ornamental fringe. The art of knotting cord or string in patterns to make decorative articles. Earliest recorded uses of macramé-style knots as decoration appeared in Babylonian and Assyrian carvings.), or flat metal adornment (
talli
Tallī: (Turkish: tel – wire, string), Gulf Arab – a woven braided trimming made with metal wire, threads and ribbons often sewn on detachable panels used as embellishments. Other – (Synonym: tulle_bi_talli
Tūlle_bi_tallī: (French: Tulle – a city in France where fine material for veil was first made; Turkish: tel – wire; Synonym: tariq; talli; badla; khus_dozi
Khus_dozi: (Persian: Khvosh – an Iranian province; dozi – needlework; Synonym: tariq; talli; tulle_bi_talli; badla), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in Iran and parts of the Arabian Peninsula possibly because Khvosh was one of the centres for the craft.
), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the North African Arab region specifically in Egypt.
; tariq; badla; khus_dozi
Khus_dozi: (Persian: Khvosh – an Iranian province; dozi – needlework; Synonym: tariq; talli; tulle_bi_talli; badla), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in Iran and parts of the Arabian Peninsula possibly because Khvosh was one of the centres for the craft.
), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment.
), that are quite similar to those found in different parts of the Arab region.
The
kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. , in particular, displays similarities that can be drawn with the pattern of Arab women’s overgarment or the (
thawb
Thawb: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thobe
Thobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. or tobe
Tobe: (Arabic: thawb, Pl. Athwāb/thībān), can be pronounced thawb or thobe based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women. based on locale. The standard Arabic word for ‘fabric’ or ‘garment’. It can also refer to a qamīs-like tunic worn by men and women in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, the southern and south-western ports and islands of Iran, and some countries in East and West Africa. More specifically, it can refer to the square-shaped Bedouin overgarment worn by women in the Arabian Gulf region. ), common to the Gulf region, constructed of three uncut panels of broad clothes forming the central body panel and the side sleeve panels very similar in shape to the
kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. .
While the tie-die (
shibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. ) technique is reminiscent of articles found in Arab countries such as (ZI2022.501006.4 SYRIA or
ZI2017.500883 SYRIA) in Syria and (ZI2021.500953.12 YEMEN or ZI2021.500953.13 YEMEN) in Yemen.
More InfoShibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. is a Japanese dyeing technique that involves creating intricate patterns on fabric by folding, twisting, and binding it before dying. Unique and beautiful patterns could be created using different binding techniques with different dyes. Some of the earliest surviving examples of
shibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. dyed fabrics like the cloth donated by Emperor Shomu to the Todai-ji Buddhist temple in Nara, Japan dates back to c. 8th century. Coupled with such examples recorded history such as written descriptions of the art or objects decorated in such art forms support the belief of its origin in Japan.
Initially it was used to dye silk for the emperors and aristocrats as well as clothes for the commoners. Different
shibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. techniques like shape resist, pole wrapping etc involve different methods of binding the fabric before dyeing resulting in unique patterns and textures. One of the most common techniques involves binding sections of the fabric with string or rubber bands to create a resist pattern. The fabric is then dyed, and the areas where the resist was applied remain undyed, creating a pattern.
It can be done with a variety of natural and synthetic dyes, including
indigo
Indigo: (Latin: Indigo – India, synonym: nil
Nīl: (Latin: indigo), Arabised term for Indigo, a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that have been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye.), a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that has been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye. . It involves creating a fermented vat of
indigo
Indigo: (Latin: Indigo – India, synonym: nil
Nīl: (Latin: indigo), Arabised term for Indigo, a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that have been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye.), a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that has been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye. , which is then used to dye the fabric. The fabric is dipped repeatedly in the
indigo
Indigo: (Latin: Indigo – India, synonym: nil
Nīl: (Latin: indigo), Arabised term for Indigo, a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that have been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye.), a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that has been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye. vat, with each dip creating a darker shade of blue. This traditional practice of using
indigo
Indigo: (Latin: Indigo – India, synonym: nil
Nīl: (Latin: indigo), Arabised term for Indigo, a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that have been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye.), a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that has been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye. for
shibori
Shibori: (Japanese: Shiboru – To wring, squeeze, or press), is a Japanese technique of manual dyeing that involves manipulating fabric to create patterns by binding, twisting, folding, or compressing it before dyeing. The history of Shibori dates back to the 8th century and has been used in the creation of a variety of fabrics, including kimono and futon covers. is quite popular even today.
Links
- Morishima, Yuki, et al. Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. Refashioned: Japan’s Impact on International Fashion. USA, Asian Art Museum, 2018.
- Kahlenberg, Mary Hunt. Asian Costumes and Textiles: From the Bosphorus to Fujiama. Italy, Skira, 2001.
- Liddell, Jill. The Story of the Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. . USA, E P Dutton, 1989.
- Dalby, Liza Crihfield. Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. : Fashioning Culture. Reaktion Books, 1993.
- Gluckman, Dale Carolyn and Sharon Sadako Takeda. When Art Became Fashion: Kosode
Kosode: (Japanese: small sleeve or opening), a traditional Japanese inner robe for both genders. Similar to a kimono but with a wider body, longer collars, and narrower and rounded sleeves, often stitched to the body, these under robes were lavishly decorated and were worn on top from late 16th century. in Edo-Period Japan. Los Angeles County Museum of Art, 1996.
- Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. : Kyoto to Catwalk. 27 Aug. – 25 Oct. 2020, V&A South Kensington, London https://www.vam.ac.uk/exhibitions/kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. -kyoto-to-catwalk
- Gluckman, Dale Carolyn. “Liza Dalby. Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. : Fashioning Culture.:Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. : Fashioning Culture.” Museum Anthropology, vol. 19, no. 1, Mar. 1995, pp. 79–81. Crossref, https://doi.org/10.1525/mua.1995.19.1.79
- “Meisen Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. From HALI 184 - HALI.” HALI, 24 July 2015, hali.com/news/meisen-kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. .
- Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. Style: Edo Traditions to Modern Design: The John C. Weber Collection. USA, Met Publications, www.metmuseum.org/art/metpublications/Kimono_Style
- Richard, Naomi Noble. “Nō Motifs in the Decoration of a Mid-Edo Period Kosode
Kosode: (Japanese: small sleeve or opening), a traditional Japanese inner robe for both genders. Similar to a kimono but with a wider body, longer collars, and narrower and rounded sleeves, often stitched to the body, these under robes were lavishly decorated and were worn on top from late 16th century. .” Metropolitan Museum Journal, vol. 25, 1990, pp. 175–83. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/1512899. Accessed 10 May 2023.
- Kramer, Elizabeth. “Review of ‘Kimono
Kimono: (Japanese: ki : wearing, mono: thing, Singular: Kimono) A traditional Japanese long loose robe with wide sleeves tied with a sash around the waist. Presently it is the national dress of Japan. : A Modern History.’” Reviews in History, School of Advanced Study, 2015. Crossref, https://doi.org/10.14296/rih/2014/1787.