Object History This object was purchased by
Dr. Reem Tariq
Ṭariq: (Arabic; Synonym: tulle_bi_talli
Tūlle_bi_tallī: (French: Tulle – a city in France where fine material for veil was first made; Turkish: tel – wire; Synonym: tariq; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the North African Arab region specifically in Egypt.
; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the Levant Arab region specifically in Lebanon.
El Mutwalli
Dr. Reem Tariq
Ṭariq: (Arabic; Synonym: tulle_bi_talli
Tūlle_bi_tallī: (French: Tulle – a city in France where fine material for veil was first made; Turkish: tel – wire; Synonym: tariq; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the North African Arab region specifically in Egypt.
; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the Levant Arab region specifically in Lebanon.
el Mutwallī: Founder (CEO) of the Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative, a public figure, speaker and author. An expert curator and consultant in Islamic art and architecture, interior design, historic costume, and UAE heritage. from an independent dealer, in Istanbul in 2021 to enhance the collection of The
Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative.
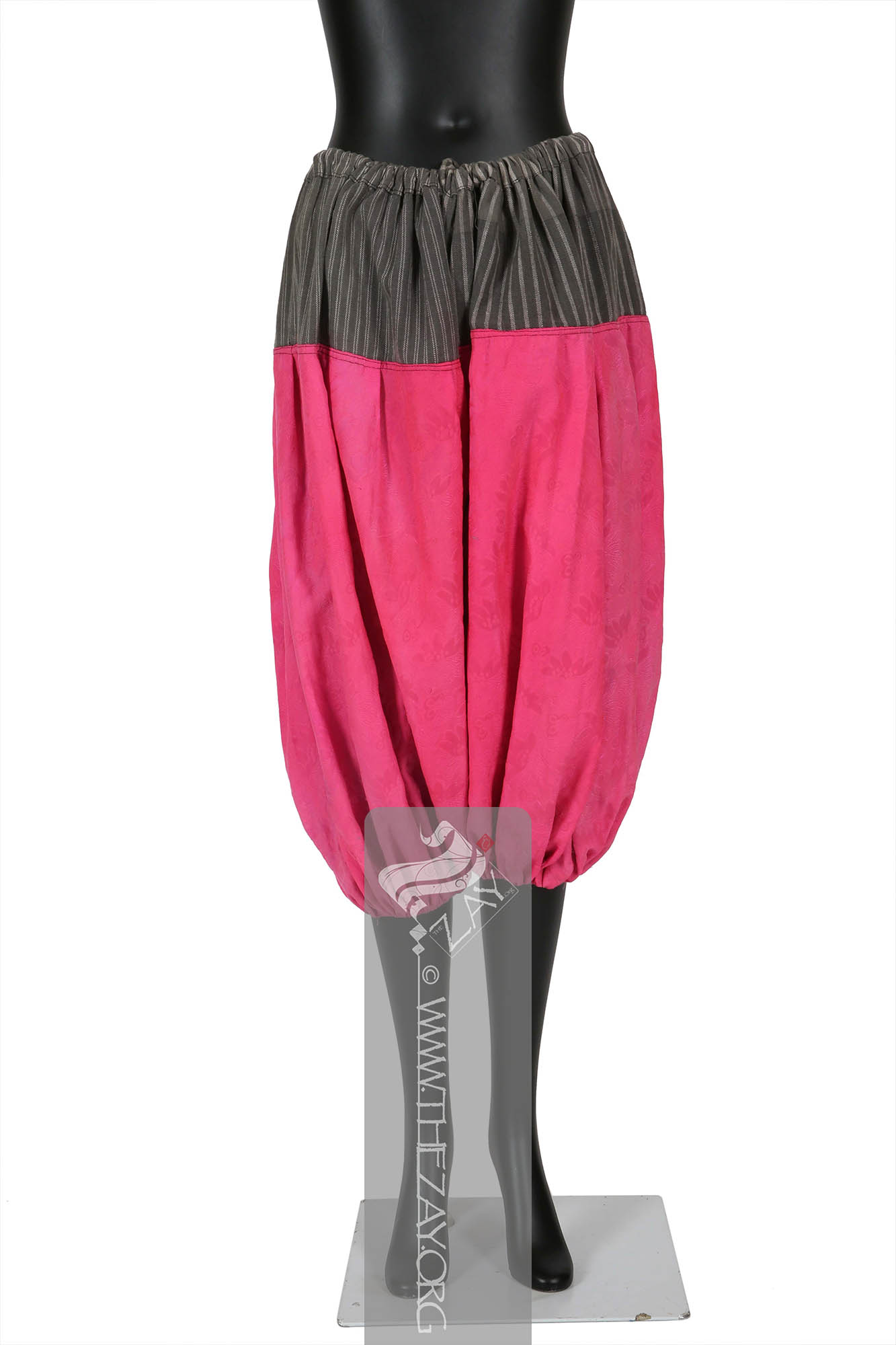
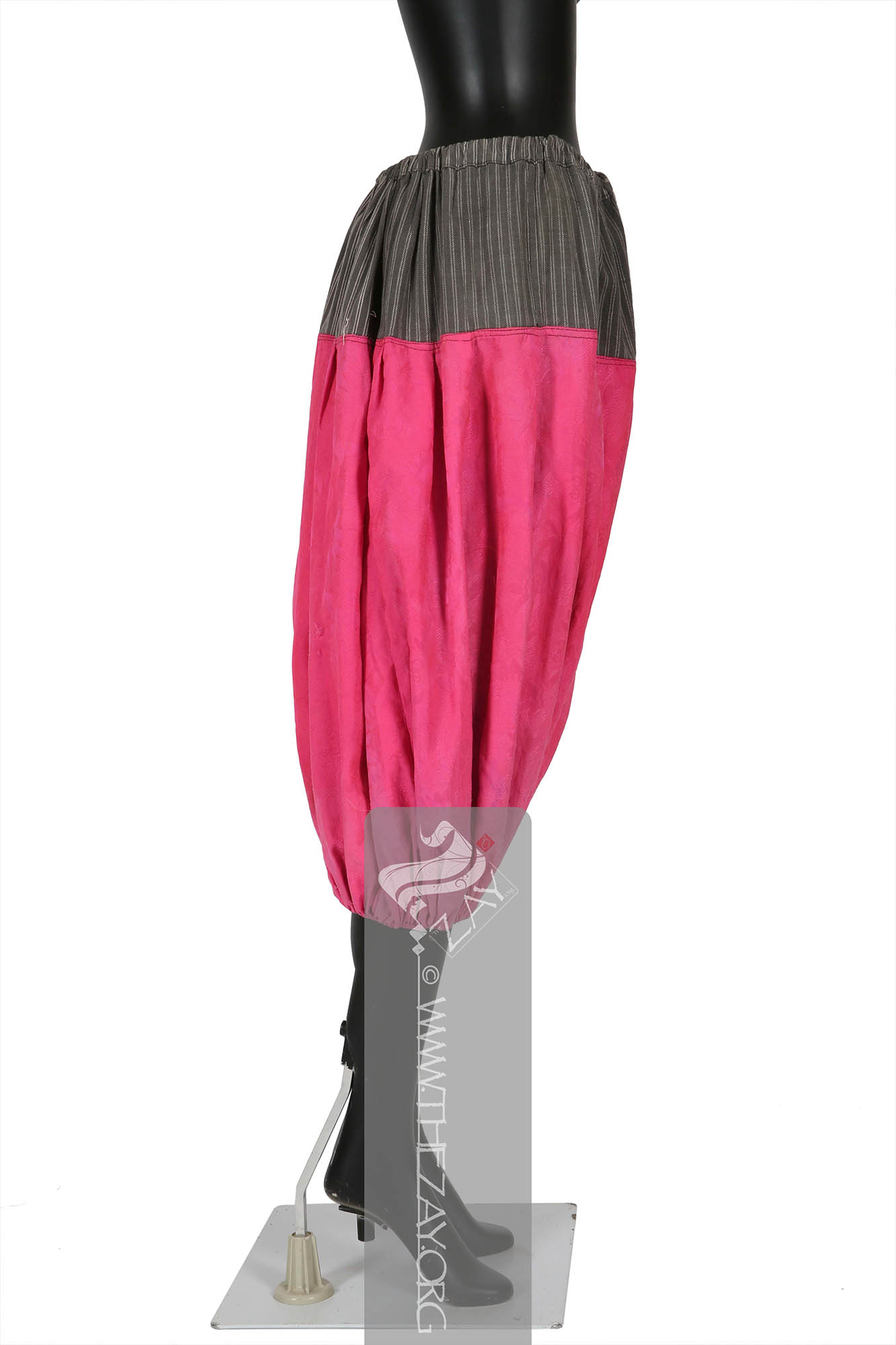
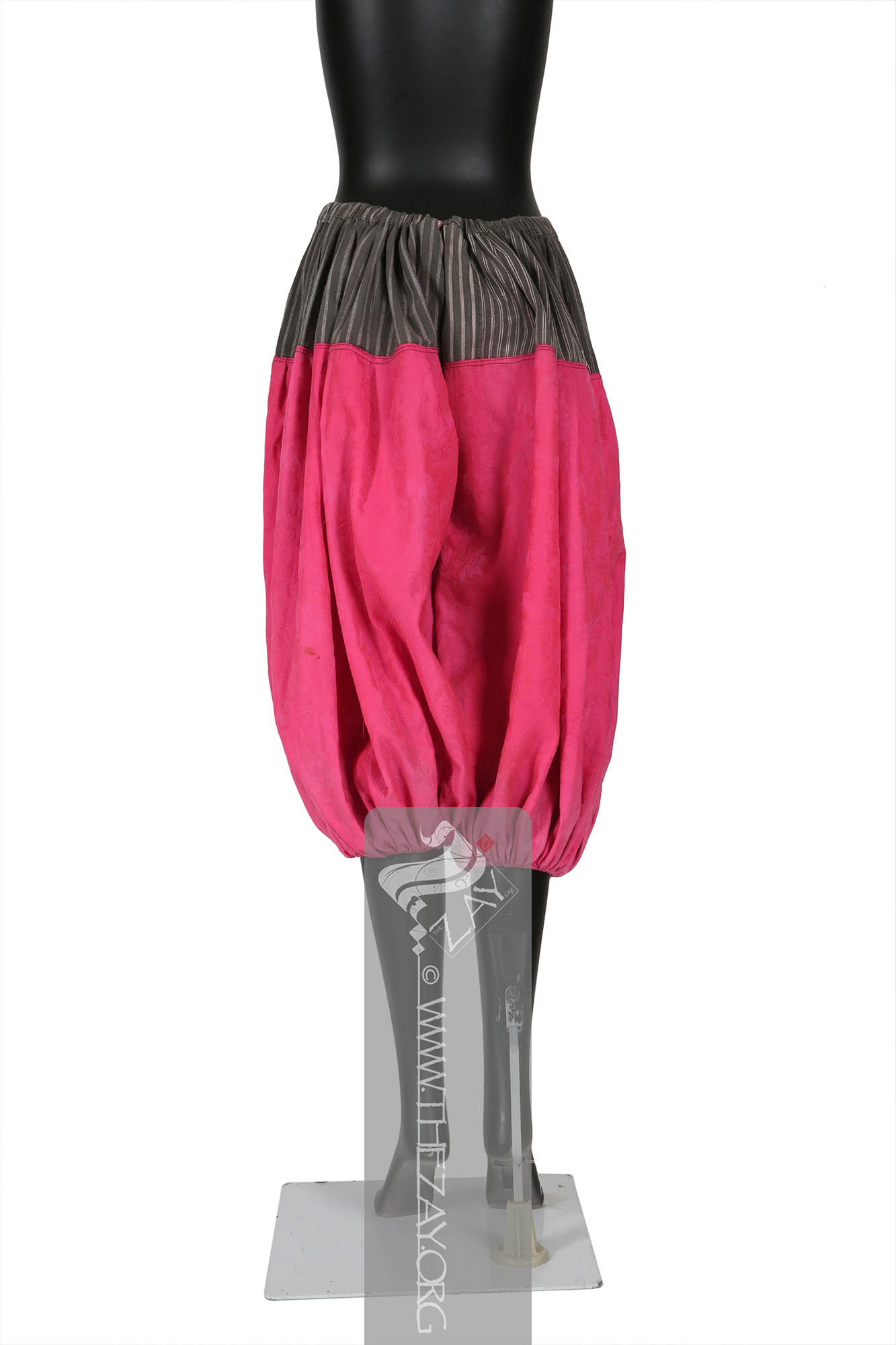
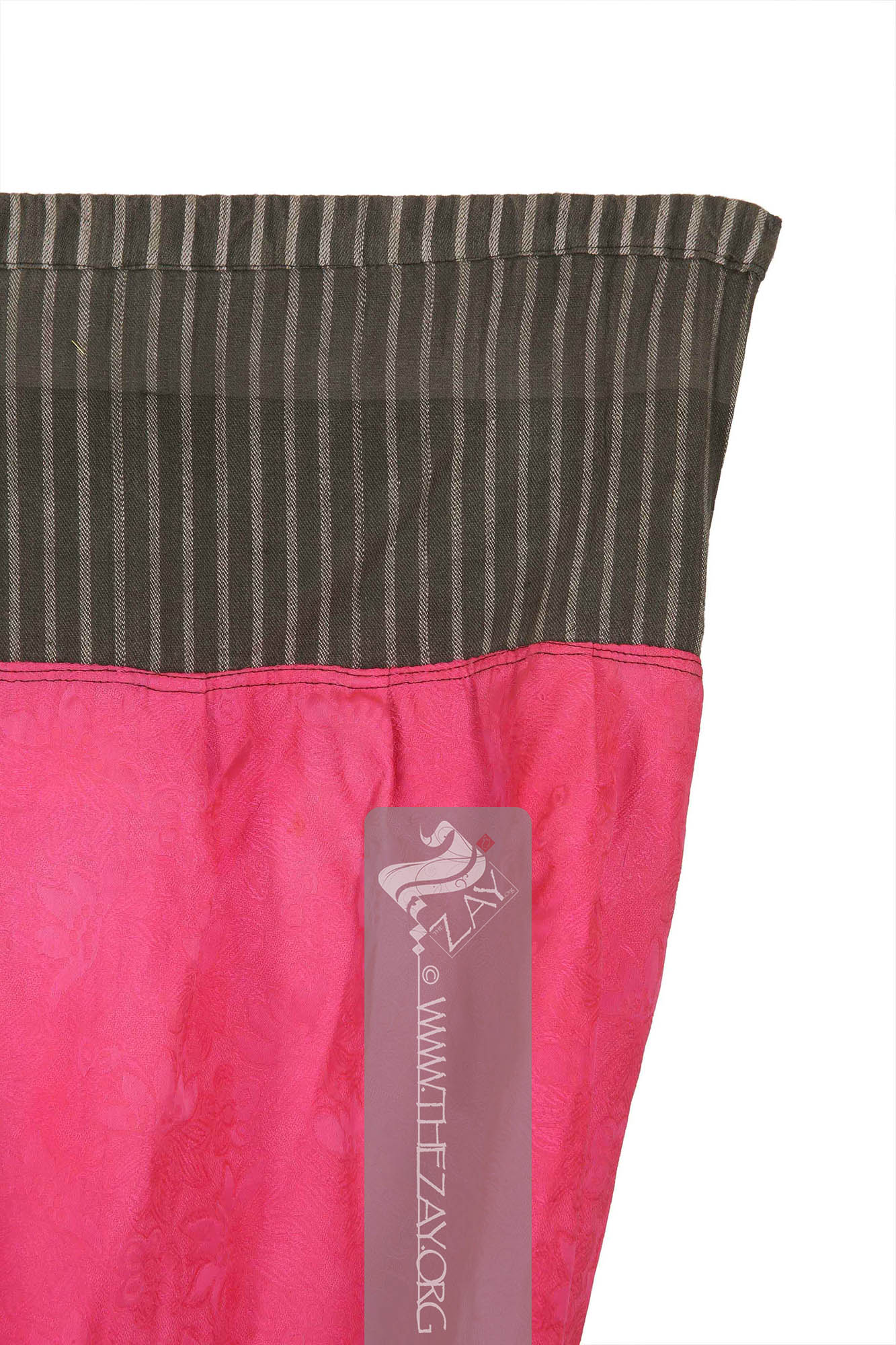
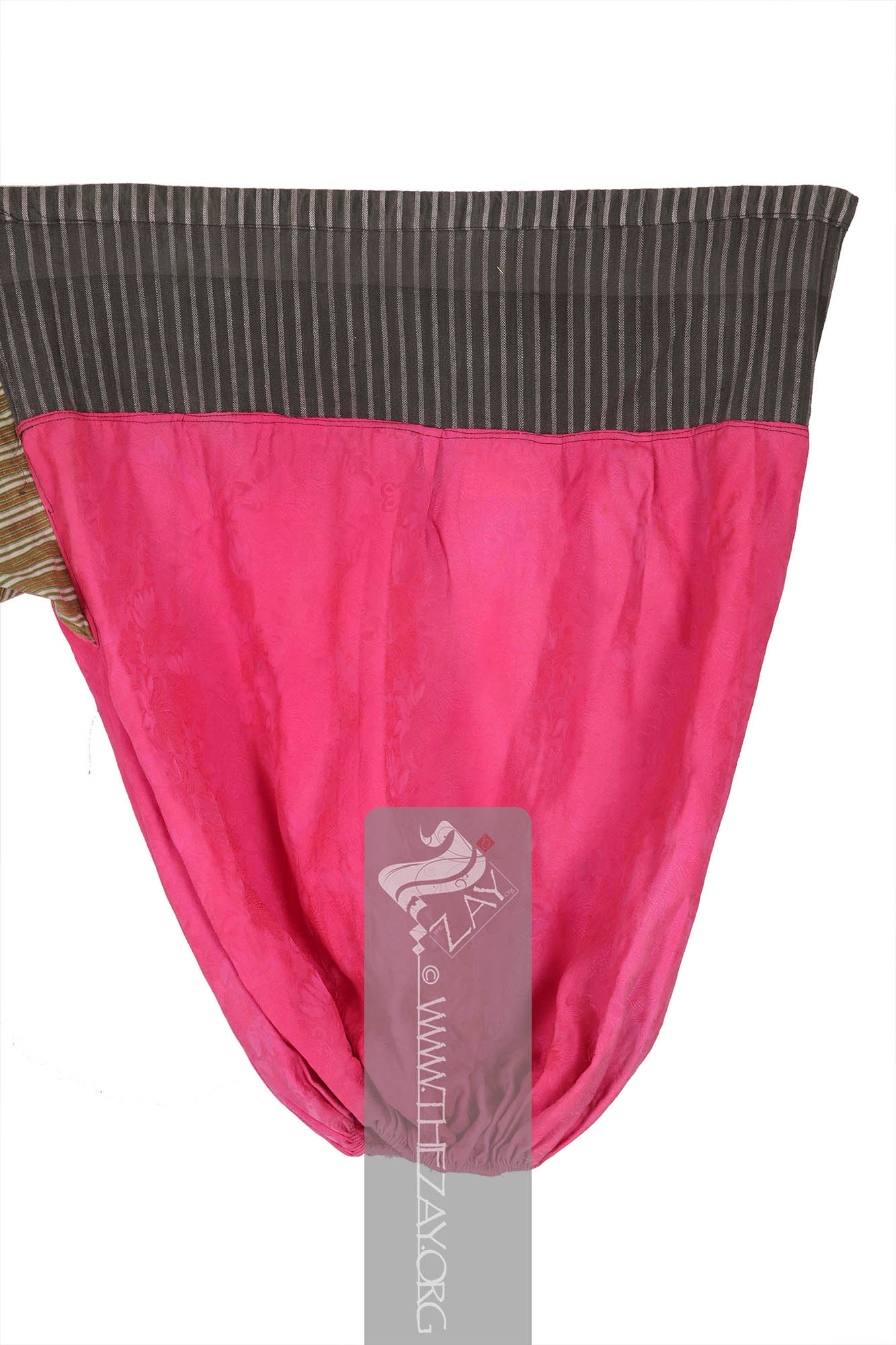
Object Features This is a pair of bright fuchsia pink calf length balloon shaped trousers (
shalvar
shalvār: in Farsi, in the Emirati colloquial: ṣarwāl. In the Levantine colloquial: Shirwāl. Plural: sarāwīl, ṣarāwīl, sharāwīl, ṣarwīlāt). It is loose pants at the waist with folds, and narrow at the ankles. It is tied with a rope at the waist.) of silk (
damask
Dāmāsk: (Arabic: Damascus – a city in Syria), is a luxurious fabric woven with reversible patterns typically in silk, wool, linen, or cotton. Originating in China, the fabric was perhaps introduced to European traders at Damascus – a major trading post on the Silk Road with a thriving local silk industry. ) fabric, with drawstring fastenings and a pair of gathered cuffs.
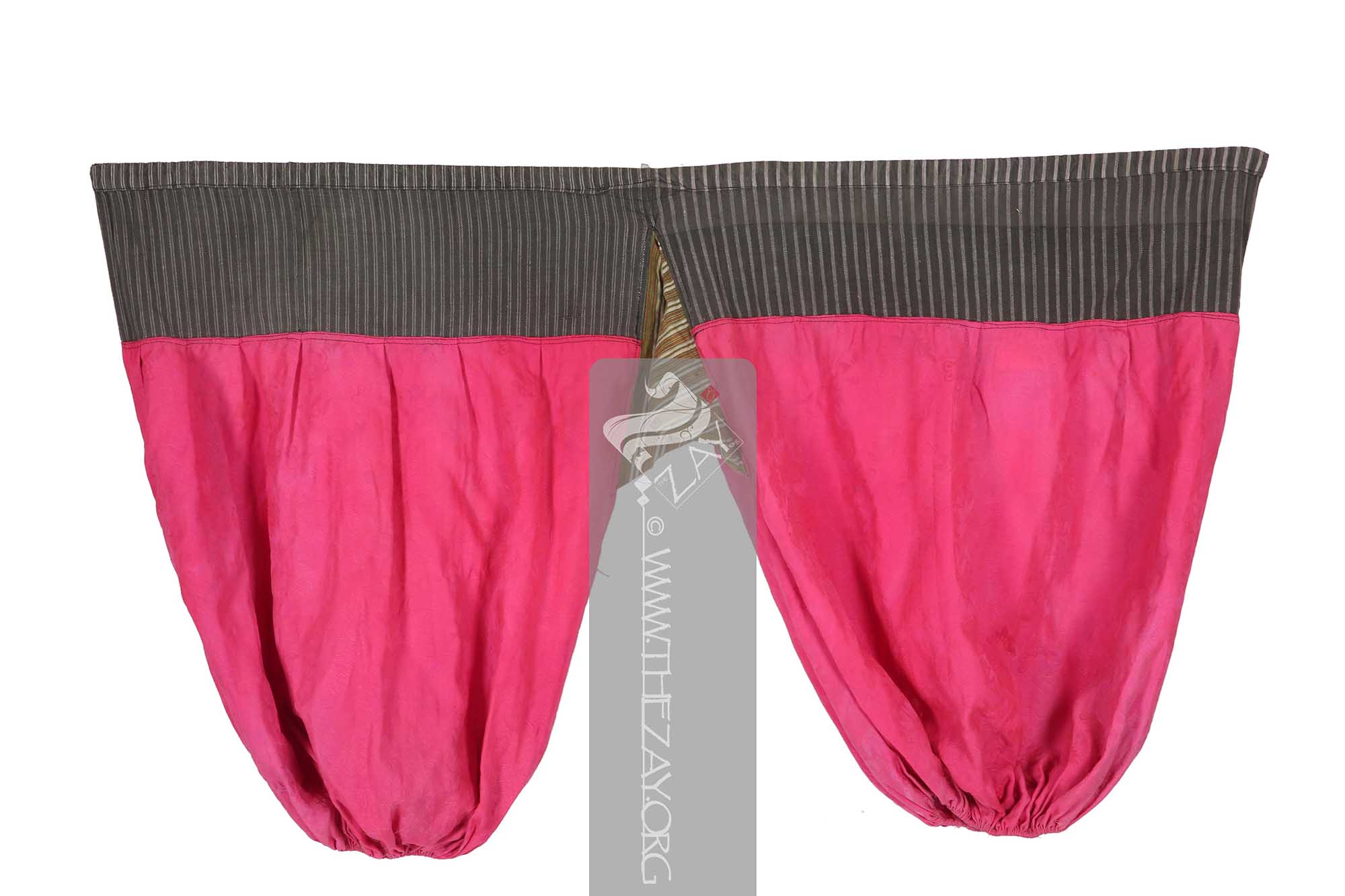
The field of the
shalvar
shalvār: in Farsi, in the Emirati colloquial: ṣarwāl. In the Levantine colloquial: Shirwāl. Plural: sarāwīl, ṣarāwīl, sharāwīl, ṣarwīlāt). It is loose pants at the waist with folds, and narrow at the ankles. It is tied with a rope at the waist. is constructed of a combination of fabrics –
damask
Dāmāsk: (Arabic: Damascus – a city in Syria), is a luxurious fabric woven with reversible patterns typically in silk, wool, linen, or cotton. Originating in China, the fabric was perhaps introduced to European traders at Damascus – a major trading post on the Silk Road with a thriving local silk industry. silk, and two different kinds of woven patterned cotton. It has a broad waist band with slots for drawstring fastenings and tightly gathered cuffs.
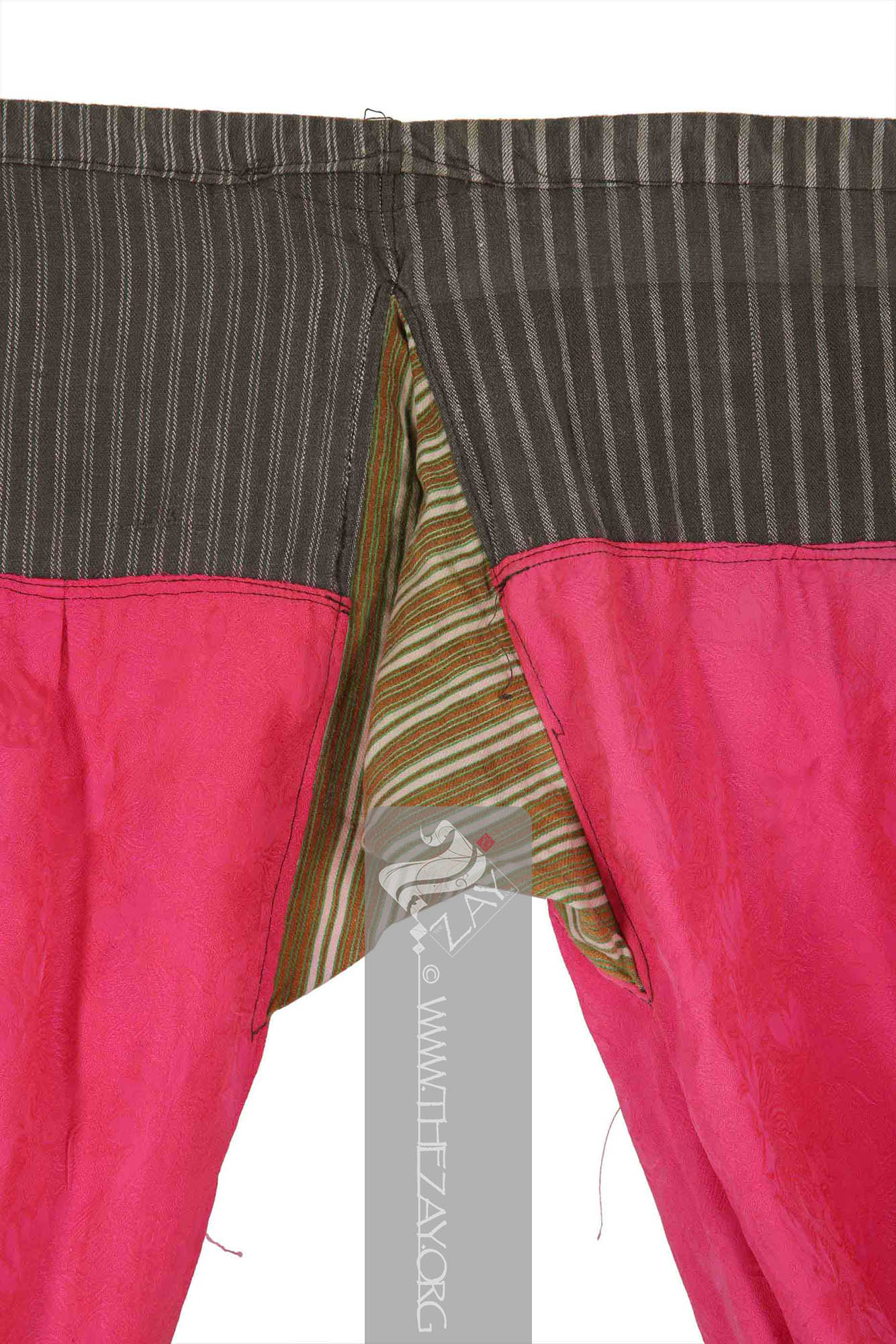
The primary field of the trousers made of the
damask
Dāmāsk: (Arabic: Damascus – a city in Syria), is a luxurious fabric woven with reversible patterns typically in silk, wool, linen, or cotton. Originating in China, the fabric was perhaps introduced to European traders at Damascus – a major trading post on the Silk Road with a thriving local silk industry. fabric features woven floral motifs as embellishments. The thick waistband linking the two legs on the top features woven stripes in ivory and grey A square piece of red green and ivory printed striped cotton fabric links the two legs in the bottom. The piece is completely machine stitched.
More InfoPrior to the widespread acceptance of European clothing in the Ottoman empire, individuals – men and women – residing in urban areas, regardless of their faith or social standing, typically adorned themselves with three primary articles of clothing.
These included a calf length cotton undershirt or (
gömlek
Gömlek: (Proto-Turkic: köyŋelek – Shirt; Azerbaijani: köynək – Shirt; Turkmen: koynek
Koynek: A traditional long, loose-fitting tunic or dress worn by Turkmen women in Central Asia typically made of silk or cotton, adorned with intricate embroidery, and often characterized by vibrant colours and geometric patterns. It is cultural symbol of significant importance reflecting the artistic heritage of Turkmen people. – long loose tunic dress), a traditional calf-length sleeved undershirt or tunic generally made of a plain white cotton, silk, or linen fabric, some more lightweight than others, worn by both Ottoman men and women of all communities throughout the empire.
), featuring long sleeves, which was worn over a pair of loose trousers known as (
shalvar
shalvār: in Farsi, in the Emirati colloquial: ṣarwāl. In the Levantine colloquial: Shirwāl. Plural: sarāwīl, ṣarāwīl, sharāwīl, ṣarwīlāt). It is loose pants at the waist with folds, and narrow at the ankles. It is tied with a rope at the waist.). Additionally, they would wear a long-sleeved robe called an
entari
: (Turkish; Synonym: Antari), a traditional Turkish long jacket-like unisex garment worn during the Ottoman era. It often featured an open front with long sleeves and was worn over an undershirt and a pair of trousers and was sometimes layered by a short waist or hip-length jacket. , reaching the ankles or floor.
Although,
entari
: (Turkish; Synonym: Antari), a traditional Turkish long jacket-like unisex garment worn during the Ottoman era. It often featured an open front with long sleeves and was worn over an undershirt and a pair of trousers and was sometimes layered by a short waist or hip-length jacket. became more and more ceremonial over the period of time, older üçetek_entari particularly for travelling served some practical purposes. Wearers would often fold and tuck the front parts into their waistband, thus creating a layering that would not just look good and assist them in moving around but also create two pouches where the wearer could store food and sometimes small stones to use with slingshots against potential attacks on the road.
Additional layers were added as necessary, based on weather conditions, social occasions, and social status. These layers encompassed items such as waistcoats, short jackets like (
cepken
Cepken: (Tartar: çepken – Outerwear; Synonyms: Shepken, Chekman, Chikmyan and other analogues in various Turkic languages with varied interpretations), short waist-length jacket traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. It usually featured full sleeves, elaborate embroidery, and a short stiff collar with front fastenings. ) and (
yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. ) or (
jilek
Jilek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. ), a short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. . ), extra
entari
: (Turkish; Synonym: Antari), a traditional Turkish long jacket-like unisex garment worn during the Ottoman era. It often featured an open front with long sleeves and was worn over an undershirt and a pair of trousers and was sometimes layered by a short waist or hip-length jacket. , as well as coats of various sizes and lengths. Belts adorned with elaborate embroidery and ornate buckles, or just embroidered sashes as (
cummerbund
Cummerbund: (Anglicized from Hindustani: kamarband
kamarband: (Persian: kamarband – a waistband or sash tied around the waist, synonym: cummerbund), a broad sash worn around the waist by men. In the 17th century, the British Indian Army adopted this style from the Indian sepoys and made it a part of the English lexicon. from Persian: kamarband
kamarband: (Persian: kamarband – a waistband or sash tied around the waist, synonym: cummerbund), a broad sash worn around the waist by men. In the 17th century, the British Indian Army adopted this style from the Indian sepoys and made it a part of the English lexicon. – a waistband or sash tied around the waist), a broad sash worn around the waist by men. In the 17th century the British Indian Army adopted this style from the Indian sepoys and made it a part of the English lexicon. ) were utilised to accentuate the bust, waist, and hips, creating a defined silhouette.
Although, the
entari
: (Turkish; Synonym: Antari), a traditional Turkish long jacket-like unisex garment worn during the Ottoman era. It often featured an open front with long sleeves and was worn over an undershirt and a pair of trousers and was sometimes layered by a short waist or hip-length jacket. was common throughout the Ottoman empire, layering with a
cepken
Cepken: (Tartar: çepken – Outerwear; Synonyms: Shepken, Chekman, Chikmyan and other analogues in various Turkic languages with varied interpretations), short waist-length jacket traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. It usually featured full sleeves, elaborate embroidery, and a short stiff collar with front fastenings. and a
yelek
Yelek: (Old Anatolian: yélek – Vest; Synonyms: Jelick, Jilek), short waist or hip length vest traditionally worn by both Ottoman men and women throughout the empire. Ranging from sleeveless to full sleeves, these vests were usually front open and without any fastenings. Often cepken jackets were used as yelek. over a
gömlek
Gömlek: (Proto-Turkic: köyŋelek – Shirt; Azerbaijani: köynək – Shirt; Turkmen: koynek
Koynek: A traditional long, loose-fitting tunic or dress worn by Turkmen women in Central Asia typically made of silk or cotton, adorned with intricate embroidery, and often characterized by vibrant colours and geometric patterns. It is cultural symbol of significant importance reflecting the artistic heritage of Turkmen people. – long loose tunic dress), a traditional calf-length sleeved undershirt or tunic generally made of a plain white cotton, silk, or linen fabric, some more lightweight than others, worn by both Ottoman men and women of all communities throughout the empire.
and a pair of loose
shalvar
shalvār: in Farsi, in the Emirati colloquial: ṣarwāl. In the Levantine colloquial: Shirwāl. Plural: sarāwīl, ṣarāwīl, sharāwīl, ṣarwīlāt). It is loose pants at the waist with folds, and narrow at the ankles. It is tied with a rope at the waist. was most common in the Balkan regions, an influence that widely spread through the rest of the Ottoman empire and was especially popular in c. late 19thand early 20th centuries in the north-western provinces such as the Marmara region in present day Türkiye, as it had a significant Balkan population.
At its peak the Ottoman Empire spanned three continents and served as the crossroads between the east and the west – the Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Eastern Europe including the Balkans till the southern edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Northern Africa and Eastern Mediterranean.
After the conquest of the Arab world in c. 1516-1517 CE its control over the Middle East lasted for four centuries until the early 20th century with the onset of WW I and the Arab Revolt. These four hundred years witnessed many instances of mutual Arab and Ottoman cultural influences and exchanges. Through areas such as social life and art – decorative and performing –we come across several instances of Arab and Turkish culture blending together through the centuries.
Just as European fashion was often inspired by the French court this socio-cultural blending between the Ottoman Turkey and the Middle East was clearly reflected in its fashion and material culture.
Thus, while emulating Ottoman fashion as the mark of class in the Arab world was one side of the puzzle adapting eastern European fashion particularly Balkan as part of mainstream couture culture because of the sizable Balkan population within the Empire was another. Therefore, it is not surprising to find several articles of clothing and their terms similar between the two cultures.
Links
- Cangökçe, Hadiye, et al. Osmanlı İmparatorluğu’nun Son Döneminden Kadın Giysileri = Women’s Costume of the Late Ottoman Era from the Sadberk Hanım Museum Collection. Sadberk Hanım Museum, 2010.
- Küçükerman, Önder, and Joyce Matthews. The Industrial Heritage of Costume Design in Turkey. GSD Foreign Trade Co. Inc, 1996.
- AĞAÇ, Saliha, and Serap DENGİN. “The Investigation in Terms of Design Component of Ottoman Women Entari
: (Turkish; Synonym: Antari), a traditional Turkish long jacket-like unisex garment worn during the Ottoman era. It often featured an open front with long sleeves and was worn over an undershirt and a pair of trousers and was sometimes layered by a short waist or hip-length jacket. in 19th Century and Early 20th Century.” International Journal of Science Culture and Sport (IntJSCS), vol. 3, no. 1, Mar. 2015, pp. 113–125. https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/91778
- Parker, Julianne. “OTTOMAN AND EUROPEAN INFLUENCE IN THE NINTEENTH-CENTURY BRIDAL COLLECTION OF THE AZEM PALACE, DAMASCUS, SYRIA.” Journal of Undergraduate Research: Brigham Young University, 18 Sept. 2013. http://jur.byu.edu/?p=6014
- Koç, Adem. “The Significance and Compatibility of the Traditional Clothing-Finery Culture of Women in Kutahya in Terms of Sustainability.” Milli Folklor , vol. 12, no. 93, Apr. 2012. 184. https://www.millifolklor.com/PdfViewer.aspx?Sayi=93&Sayfa=181
- Micklewright, Nancy. “Late-Nineteenth-Century Ottoman Wedding Costumes as Indicators of Social Change.” Muqarnas, vol. 6, 1989, pp. 161–74. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/1602288. Accessed 13 July 2023.
- Micklewright, Nancy. “Looking at the Pst: Nineteenth Century Images of Constantinople and Historic Documents.” Expedition, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 24–32. https://www.penn.museum/documents/publications/expedition/pdfs/32-1/micklewright.pdf
- Ozgen, Ozlen, et al. “Henna Ritual Clothing in Anatolia from Past to Present: An Evaluation on Bindalli.” Textile Society of America Symposium Proceedings, 2021, https://doi.org/10.32873/unl.dc.tsasp.0122.
- Denny, Walter B., and Sumru Belger Krody. The Sultan’s Garden: The Blossoming of Ottoman Art. The Textile Museum, 2012. https://museum.gwu.edu/sites/g/files/zaxdzs3226/f/Sultans%20Garden%20Catalogue.pdf
- Ersoy, Ayla. Traditional Turkish Arts. Ministry of Culture and Tourism Publications, 2008. https://teda.ktb.gov.tr/Eklenti/6593,traditionalturkishartspdf.pdf
- https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/
- https://collections.vam.ac.uk/
- https://www.metmuseum.org/art/
- https://www.metmuseum.org/art/
- https://islamicart.museumwnf.org
- https://www-kutahya-gov-tr.translate.goog/geleneksel-giysi
- https://archive.aramcoworld.com/issue/200703/the.skill.of.the.two.hands.htm
- http://www.turkishculture.org/textile-arts/clothing/womens-garments/womens-garments
- http://jezebeljane.blogspot.com/2015/09/womens-clothing-in-16th-century-turkey
- https://www.issendai.com/16thcenturyistanbul/visual-dictionary/kaftan/
- https://babogenglish.wordpress.com/2016/02/25/turkey-general-information/
- https://ertugrulforever.com/turkish-fashion-2021/
- https://northamericaten.com/turkish-clothing-of-ottoman-times/
- https://www.al-monitor.com/originals/2019/04/turkish-traditional-costumes-from-head-to-toe