Object historyNot much is known about this object, as it was found packed away and stored in an old cedar chest, where it sat for many years, protected from light before being sold to
Dr. Reem Tariq
Ṭariq: (Arabic; Synonym: tulle_bi_talli
Tūlle_bi_tallī: (French: Tulle – a city in France where fine material for veil was first made; Turkish: tel – wire; Synonym: tariq; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the North African Arab region specifically in Egypt.
; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the Levant Arab region specifically in Lebanon.
El Mutwalli
Dr. Reem Tariq
Ṭariq: (Arabic; Synonym: tulle_bi_talli
Tūlle_bi_tallī: (French: Tulle – a city in France where fine material for veil was first made; Turkish: tel – wire; Synonym: tariq; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the North African Arab region specifically in Egypt.
; talli; badla; khus_dozi ), series of small metal knots made on a woven net ground as embellishment. The term is commonly used in the Levant Arab region specifically in Lebanon.
el Mutwallī: Founder (CEO) of the Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative, a public figure, speaker and author. An expert curator and consultant in Islamic art and architecture, interior design, historic costume, and UAE heritage. by a dealer from the United States in 2018 and was added to The
Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Collection.
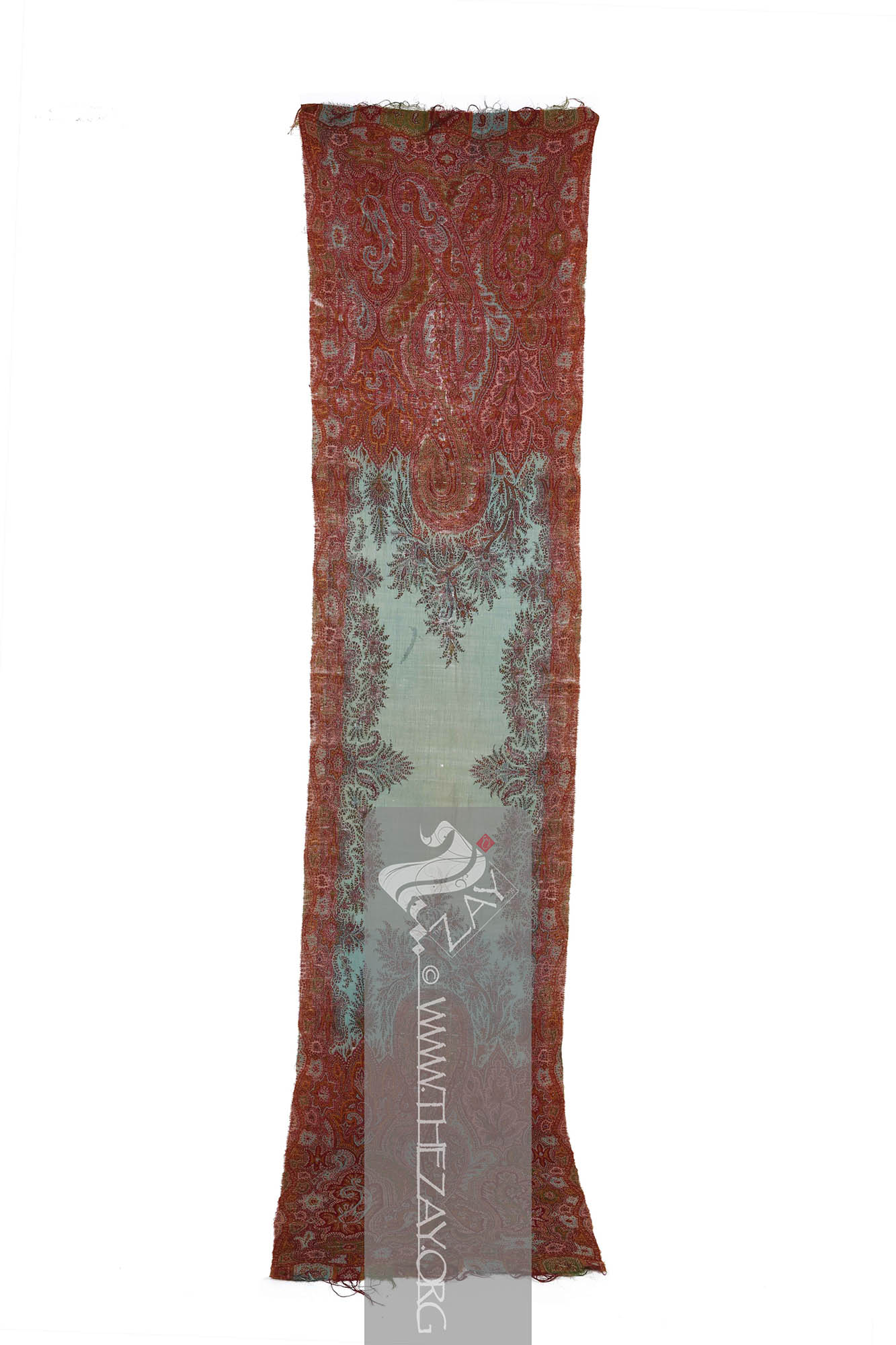
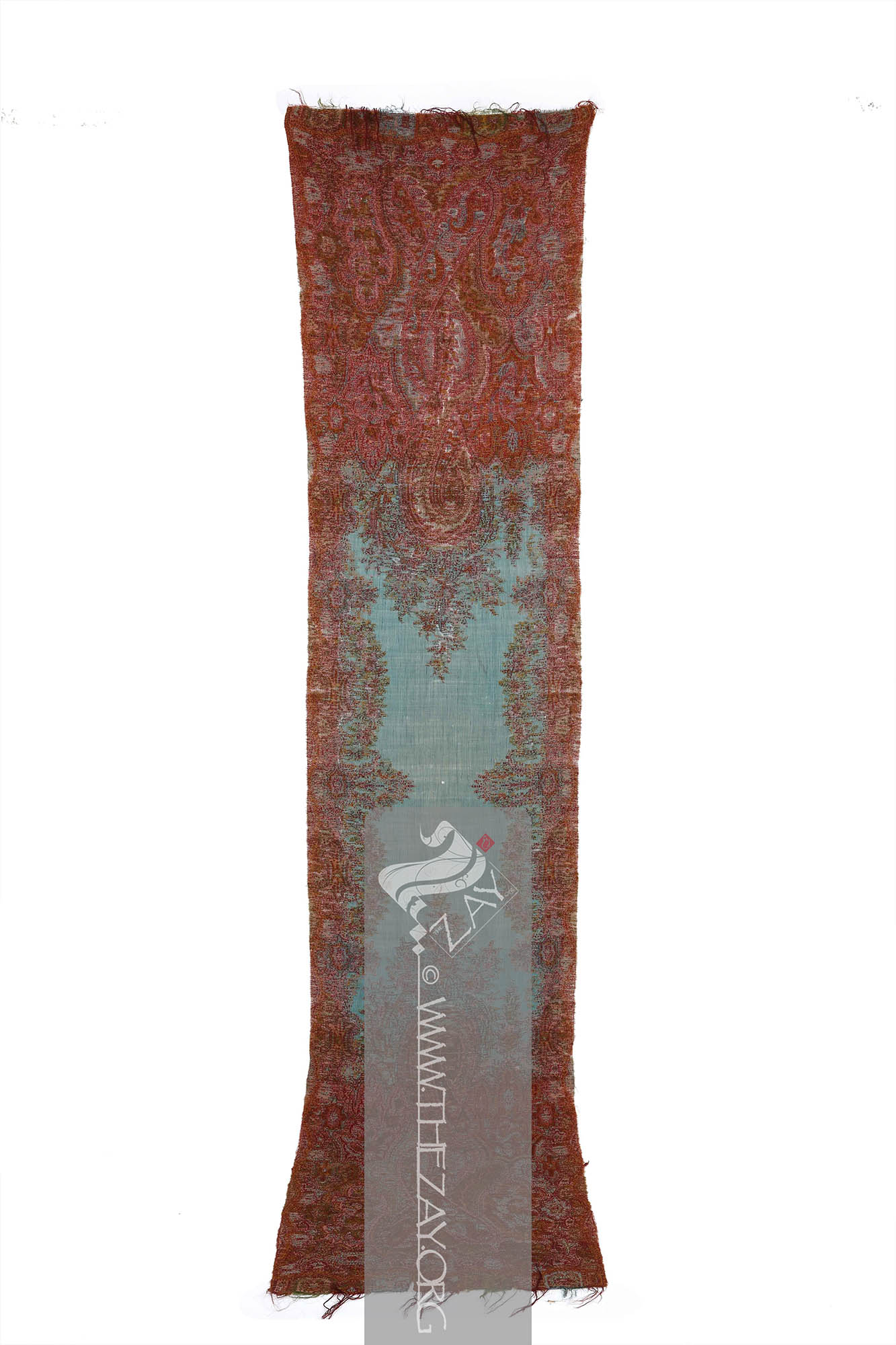
Object Features This is a narrow rectangular piece of woollen fabric – (
cashmere
Cashmere: (Anglisized from Hindustani: Kashmir – A region or province in the Indian subcontinent), a fine soft natural wool, from the hair of goats native to the Kashmir, Ladakh and neighbouring regions of the Indian subcontinent. Often confused with Pashmina
Pāshmīna: (Persian: pašm or pashm – wool), pashmina scarves are eponymous woolen shawls from the Kashmir region with a history dating back to more than 500 years. It is the finest variant of spun cashmere wool extracted from the downy undercoat of the Changthangi goats found in the Ladakh province. , it should be noted that all cashmeres are not pashmina
Pāshmīna: (Persian: pašm or pashm – wool), pashmina scarves are eponymous woolen shawls from the Kashmir region with a history dating back to more than 500 years. It is the finest variant of spun cashmere wool extracted from the downy undercoat of the Changthangi goats found in the Ladakh province. . ) most probably of the (
pashmina
Pāshmīna: (Persian: pašm or pashm – wool), pashmina scarves are eponymous woolen shawls from the Kashmir region with a history dating back to more than 500 years. It is the finest variant of spun cashmere wool extracted from the downy undercoat of the Changthangi goats found in the Ladakh province. ) variety – in (
kani
Kani: (Kashmiri
Kashmiri: (Hindustani: Kashmir – a region in South Asia), a term used to denote or identify anything related to the region – its people, their language, culture, art and craft, society etc. : Small sticks, also a name of a village in Kashmir), a type of weave that originated in this village where wooden bobbins or sticks are used as spools on the loom to create intricate patterns instead of a shuttle.
) weave. With both elaborate yet intricate design, its wool variety, and its weave this exquisite piece indicates its origin to be possibly Kashmir.
Handwoven on a loom
selvedge
Selvedge: (English: Self-finished edge or self-edge: a dialect forming transition), an edge produced on woven fabric during manufacture that prevents it from unravelling. Traditionally the term selvage applied to only loom woven fabric, presently it could be applied to flat knitted fabric too. to
selvedge
Selvedge: (English: Self-finished edge or self-edge: a dialect forming transition), an edge produced on woven fabric during manufacture that prevents it from unravelling. Traditionally the term selvage applied to only loom woven fabric, presently it could be applied to flat knitted fabric too. this piece has no extra attachments.
The item is woven in two most dominant colours – (
turquoise
Turquoise: (French: turquois – present day Türkiye; Synonyms: firuze, pheroza), is a naturally occurring opaque mineral mined in abundance in Khorasan province of Iran and has been used for making dye for centuries. The term is a derivative of the French word for the country Türkiye once called Turkey. ) blue or (
pheroza
: (Persian: pērōzah – "victory", later Arabic: fayrūz; Synonyms: firuze, turquoise
Turquoise: (French: turquois – present day Türkiye; Synonyms: firuze, pheroza), is a naturally occurring opaque mineral mined in abundance in Khorasan province of Iran and has been used for making dye for centuries. The term is a derivative of the French word for the country Türkiye once called Turkey. ), is a naturally occurring opaque mineral mined in abundance in Khorasan province of Iran and has been used for making dye for centuries. ) which forms the base and the plain centre and (
madder
Madder: (Latin: Rubia tinctorum – Eurasian herb), rose madder, common madder or dyer's madder is a vegetable dye made from the roots of a perennial plant belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family. It has been used extensively as a vegetable red dye across the globe from India to England.
) red for the elaborate and beautiful design with highlights of moss green and
pheroza
: (Persian: pērōzah – "victory", later Arabic: fayrūz; Synonyms: firuze, turquoise
Turquoise: (French: turquois – present day Türkiye; Synonyms: firuze, pheroza), is a naturally occurring opaque mineral mined in abundance in Khorasan province of Iran and has been used for making dye for centuries. The term is a derivative of the French word for the country Türkiye once called Turkey. ), is a naturally occurring opaque mineral mined in abundance in Khorasan province of Iran and has been used for making dye for centuries. .
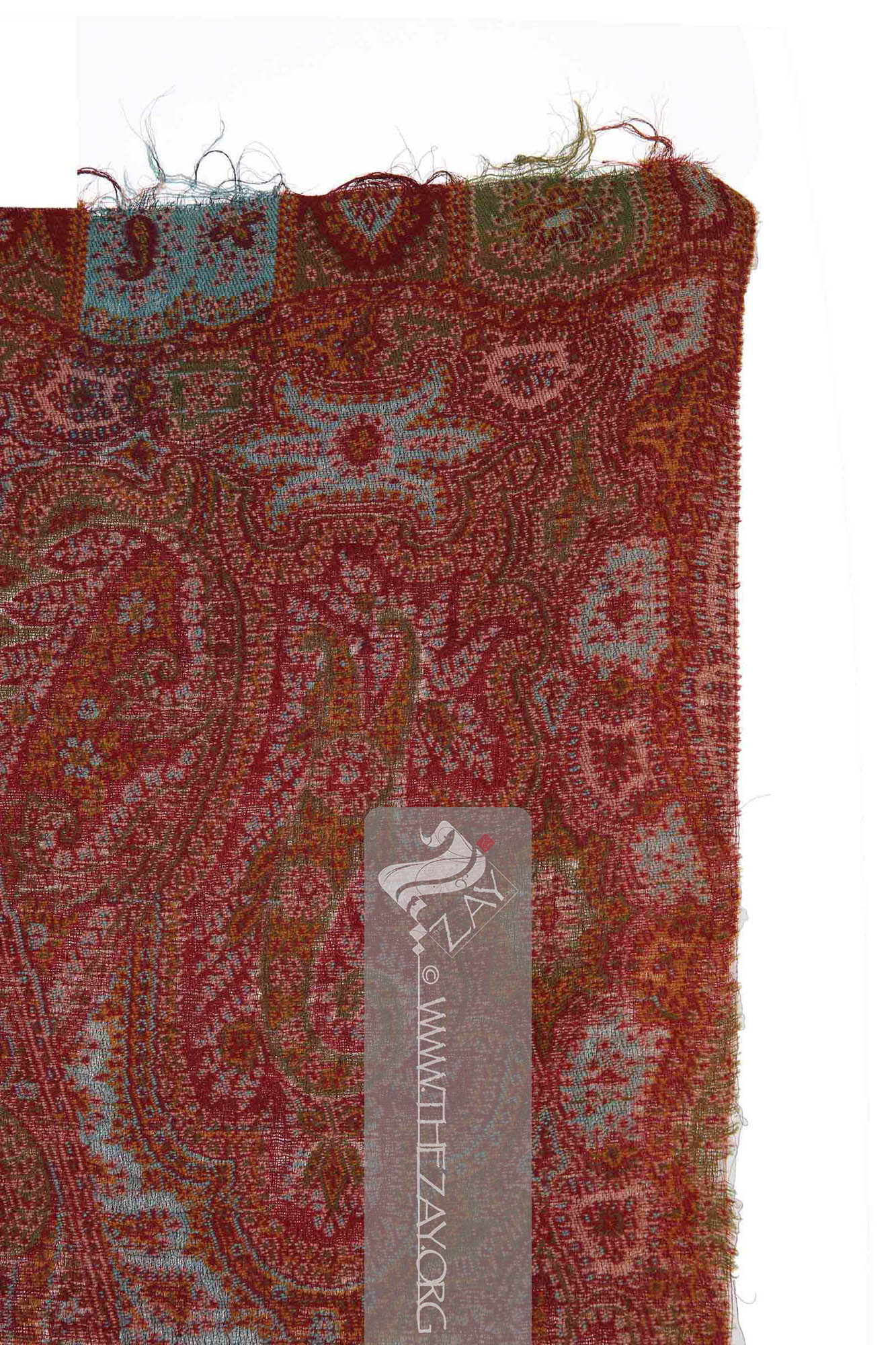
The (
warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. ) ends are decorated with alternating blue and green scalloped arches punctuated with a red arch in between forming the border. The blue and green arches are filled with similar elements – floral arrangements and a (
paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature.) – in a mirroring orientation, while the red arches are filled with a floral (
palmette
Palmette: (French: Palmette – Small palm, synonym Greco-Roman: Anthemion), a decorative element, motif, or ornament particularly pertaining to designs of architecture and decorative arts that has radiating petals resembling a palm leaf. It is believed to have originated in ancient Egypt and had subsequently reached far and wide. ) design. It is concluded with a row of polychromatic fringes.
There is no specific (
tanjir
Tanjīr: (Possibly Persian: zanjir: Chain), a narrow layer of pattern that forms the border and runs above and below the wider layer. ) to distinguish the broader than usual (
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . ) from the central body of the piece. Thus, the
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . in a crisscross and overlapping arrangements of paisleys and floral vines mostly in red with sporadic sprinkles of
turquoise
Turquoise: (French: turquois – present day Türkiye; Synonyms: firuze, pheroza), is a naturally occurring opaque mineral mined in abundance in Khorasan province of Iran and has been used for making dye for centuries. The term is a derivative of the French word for the country Türkiye once called Turkey. highlights extends and merges itself with the central elements on both sides.
The centre is primarily plain except a frame of floral vines that seem to emerge from the borders and
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . on either side. The vines on the
warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. ends are long and curvy with intricate foliage, while the
weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. ends have curved vines of foliage with a central bouquet flanked by two paisleys.
Although not much is known about the origin and provenance of this piece it could be safely concluded from the absence of clear (
selvedge
Selvedge: (English: Self-finished edge or self-edge: a dialect forming transition), an edge produced on woven fabric during manufacture that prevents it from unravelling. Traditionally the term selvage applied to only loom woven fabric, presently it could be applied to flat knitted fabric too. ) that this item was perhaps a part of mass production of several items of a similar kind made on the same loom. The long narrow size indicates that it was woven as an accessory – a (
cummerbund
Cummerbund: (Anglicized from Hindustani: kamarband
kamarband: (Persian: kamarband – a waistband or sash tied around the waist, synonym: cummerbund), a broad sash worn around the waist by men. In the 17th century, the British Indian Army adopted this style from the Indian sepoys and made it a part of the English lexicon. from Persian: kamarband
kamarband: (Persian: kamarband – a waistband or sash tied around the waist, synonym: cummerbund), a broad sash worn around the waist by men. In the 17th century, the British Indian Army adopted this style from the Indian sepoys and made it a part of the English lexicon. – a waistband or sash tied around the waist), a broad sash worn around the waist by men. In the 17th century the British Indian Army adopted this style from the Indian sepoys and made it a part of the English lexicon. ) or girdle more commonly known as a (
patka
: (Sanskrit: paṭṭikā – a ligature or strip of cloth; Pataka – A ribbon or girdle or piece of cloth; Synonym – Patako), a sash or waistband worn by men and tied with their ends hanging down the front or a piece of often square shaped cloth worn underneath a turban in South Asia. ) in the subcontinent – and not a full
shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . This serves as another indication of its place of origin as girdles of this kind were used only around the subcontinent and had no use of being woven in the looms of Europe.
Apart from a very tiny hole in the blue central section, and a small one-inch tear at one end, this
shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. is in fairly good condition.