Object HistoryThis rectangular (
long_shawl
Long_Shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. : (Synonym: Kirking Shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. ), European versions of and inspired by Kashmiri double shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. s in wool or silk manufactured locally in Europe. As a part of the trousseau for aristocratic women, it was often used at their first post-wedding church services and christenings. ) dating back to the early 19th century was originally a part of the Dr Joan Coleman Collection. It was first purchased at a Phillips auction on March 27, 1991. Later The
Zay
Zay: (Arabic: costume, Pl. azyaā’), a set of clothes in a style typical of a particular country or historical period. Initiative managed to acquire it from Kerry Taylor Auctions in 2020.
Dr Joan Coleman began collecting shawls in 1976 and developed her lifelong passion for collecting. She was a regular at the London salesrooms of Christie’s, Sotheby’s, and Phillips – three of the most outstanding auction houses of the period in the world – getting to know the dealers and learning in the process. She acquired vast knowledge and dedicated hours carefully cataloguing her ever-growing collection. She intended to loan her collection to different museums and institutions for the benefit of learning and education. Her collection is one of the largest and the finest private
shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. collections to have ever graced the world with shawls ranging from Kashmir,
Paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature., Edinburgh, Norwich, France, and Iran.
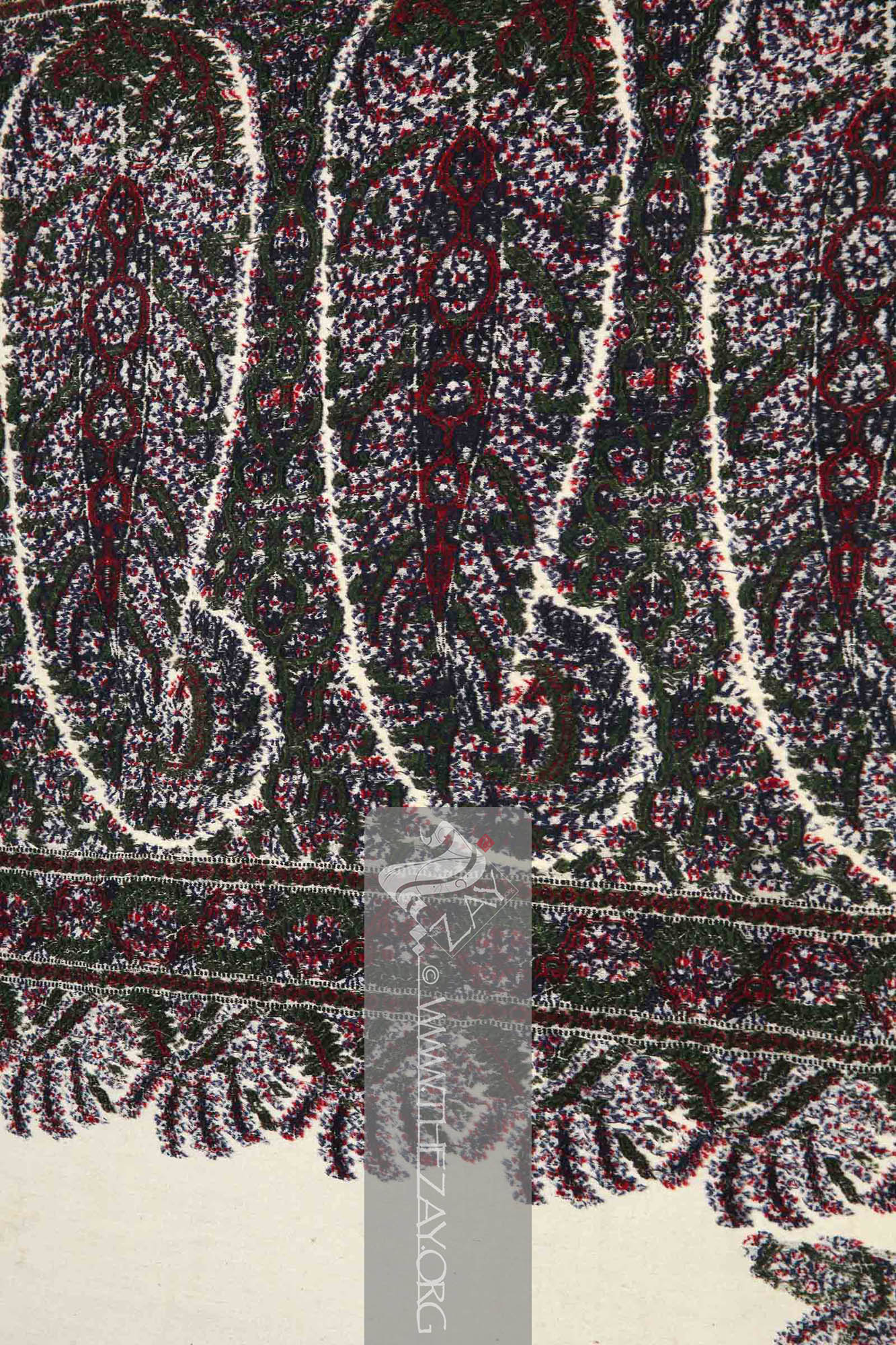
Object Features This beautiful
long_shawl
Long_Shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. : (Synonym: Kirking Shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. ), European versions of and inspired by Kashmiri double shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. s in wool or silk manufactured locally in Europe. As a part of the trousseau for aristocratic women, it was often used at their first post-wedding church services and christenings. manufactured in
Paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature. Scotland, c. 1835 is primarily woven in ivory, green, red and (
indigo
Indigo: (Latin: Indigo – India, synonym: nil
Nīl: (Latin: indigo), Arabised term for Indigo, a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that have been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye.), a natural dye belonging to the ‘Indigofera Tinctoria’ species of plants that has been cultivated in East Asia, Egypt, India, and Peru since antiquity. According to Pliny the Elder, it was named after India as it was the source of the dye. ) blue. Although identified as wool – the primary fabric in ivory – in its acquisition receipt by its previous collector – Kerry Taylor – it could be safely concluded as the silk of (
satin
Sātin: (Arabic: Zaytuni: from Chinese port of Zayton in Quanzhou province where it was exported from and acquired by Arab merchants), one of the three basic types of woven fabric with a glossy top surface and a dull back. Originated in China and was fundamentally woven in silk.) weave upon closer perusal. The estimated year of manufacturing and its (
selvedge
Selvedge: (English: Self-finished edge or self-edge: a dialect forming transition), an edge produced on woven fabric during manufacture that prevents it from unravelling. Traditionally the term selvage applied to only loom woven fabric, presently it could be applied to flat knitted fabric too. ) to
selvedge
Selvedge: (English: Self-finished edge or self-edge: a dialect forming transition), an edge produced on woven fabric during manufacture that prevents it from unravelling. Traditionally the term selvage applied to only loom woven fabric, presently it could be applied to flat knitted fabric too. weaving concludes that it was produced in a (
jacquard
Jacquard: (After Joseph M Jacquard a French weaver and inventor), is referred to both an apparatus with perforated cards invented by the aforementioned Joseph M Jacquard in 1804 fitted to a loom enabling complex intricate weaving patterns and the brocaded fabric woven on a jacquard loom. ) loom.
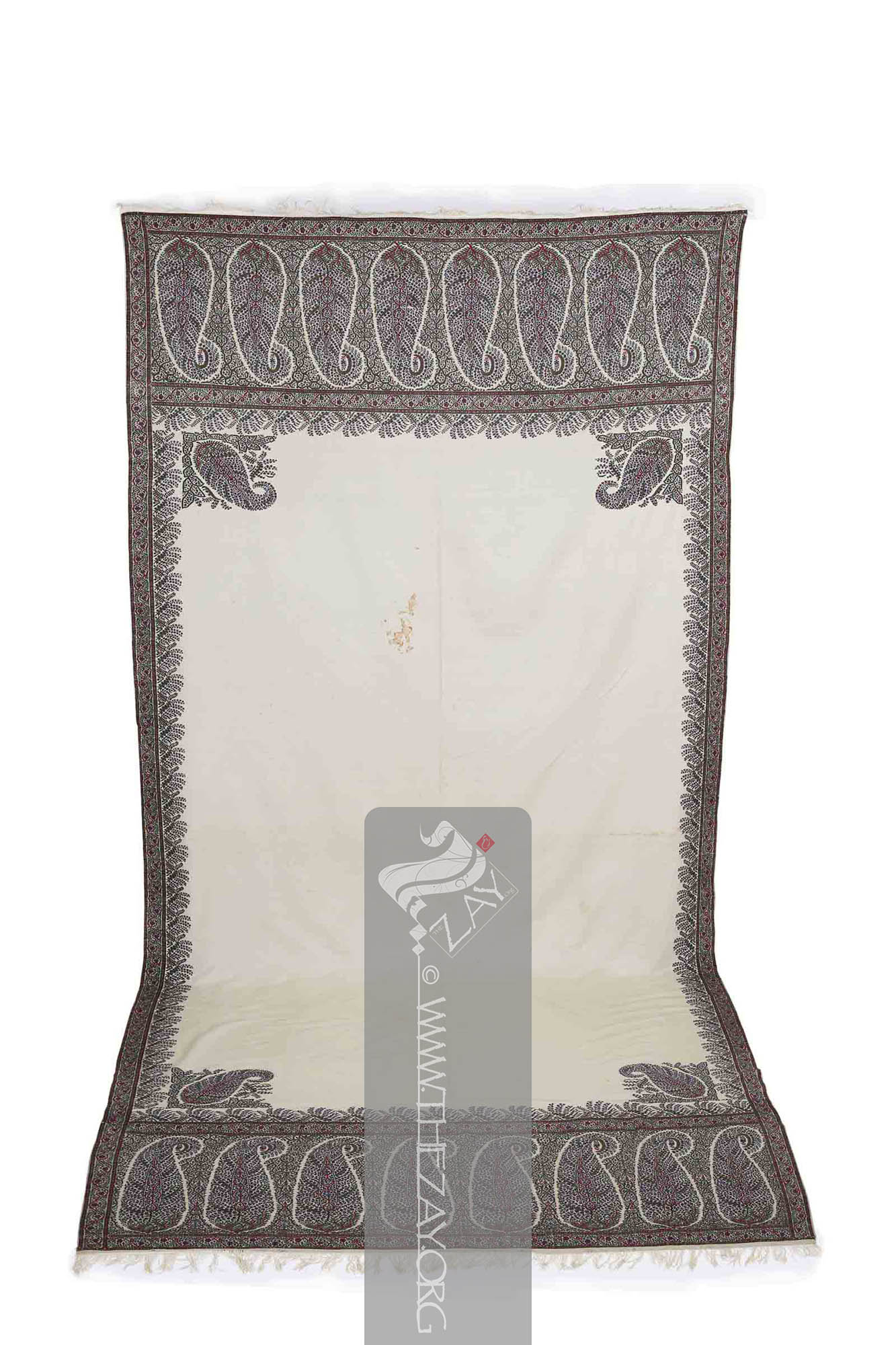
It is a typical (
kirking_shawl
Kirking_shawl: (Scottish: Kirk from Old English: cirice – Church; Synonym: Long Shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. ), European versions of and inspired by Kashmiri double shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. s in wool or silk manufactured locally in Europe. As a part of the trousseau for aristocratic women, it was often used at their first post-wedding church services and christenings. ) of its era with a pair of (
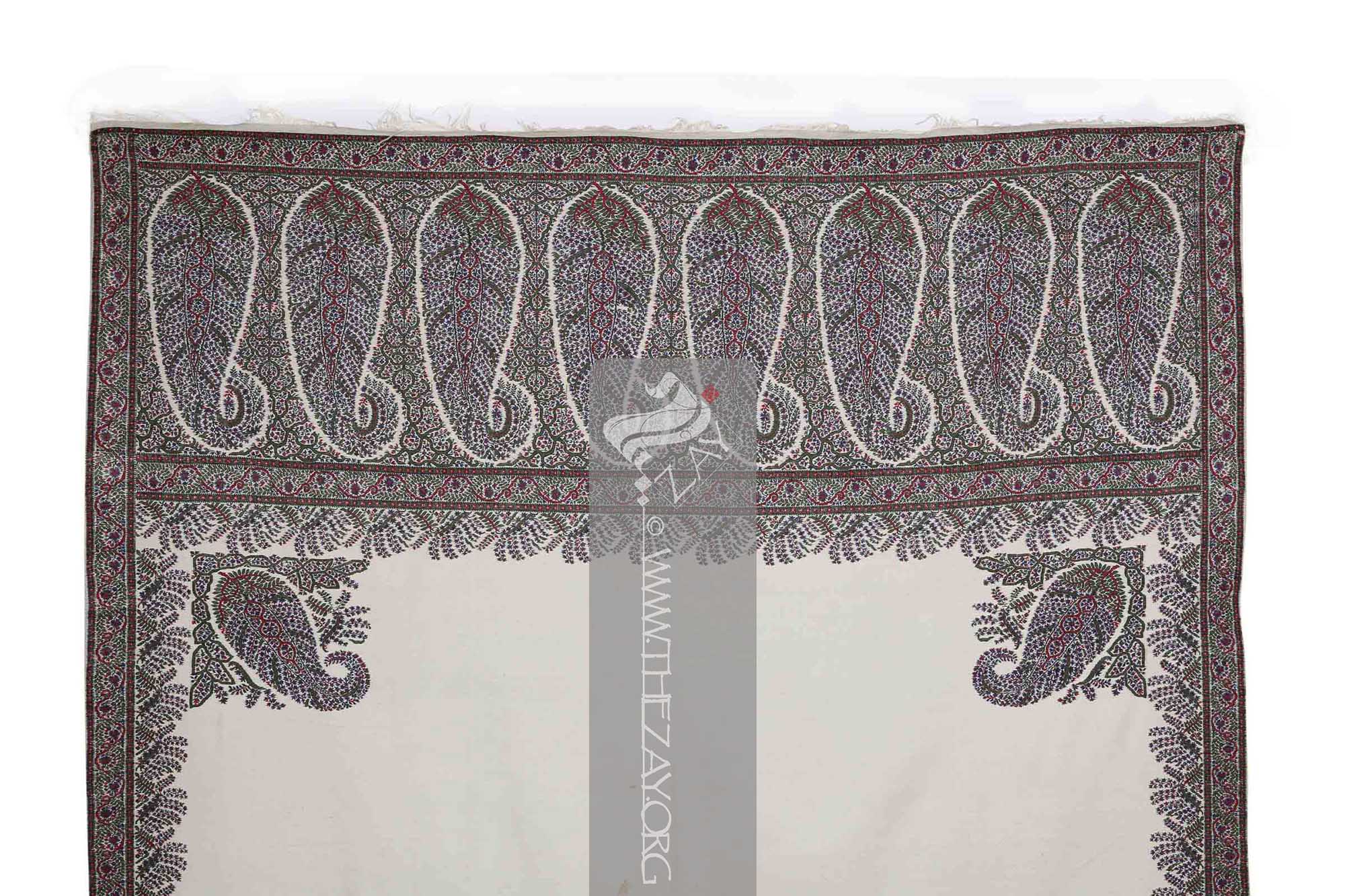
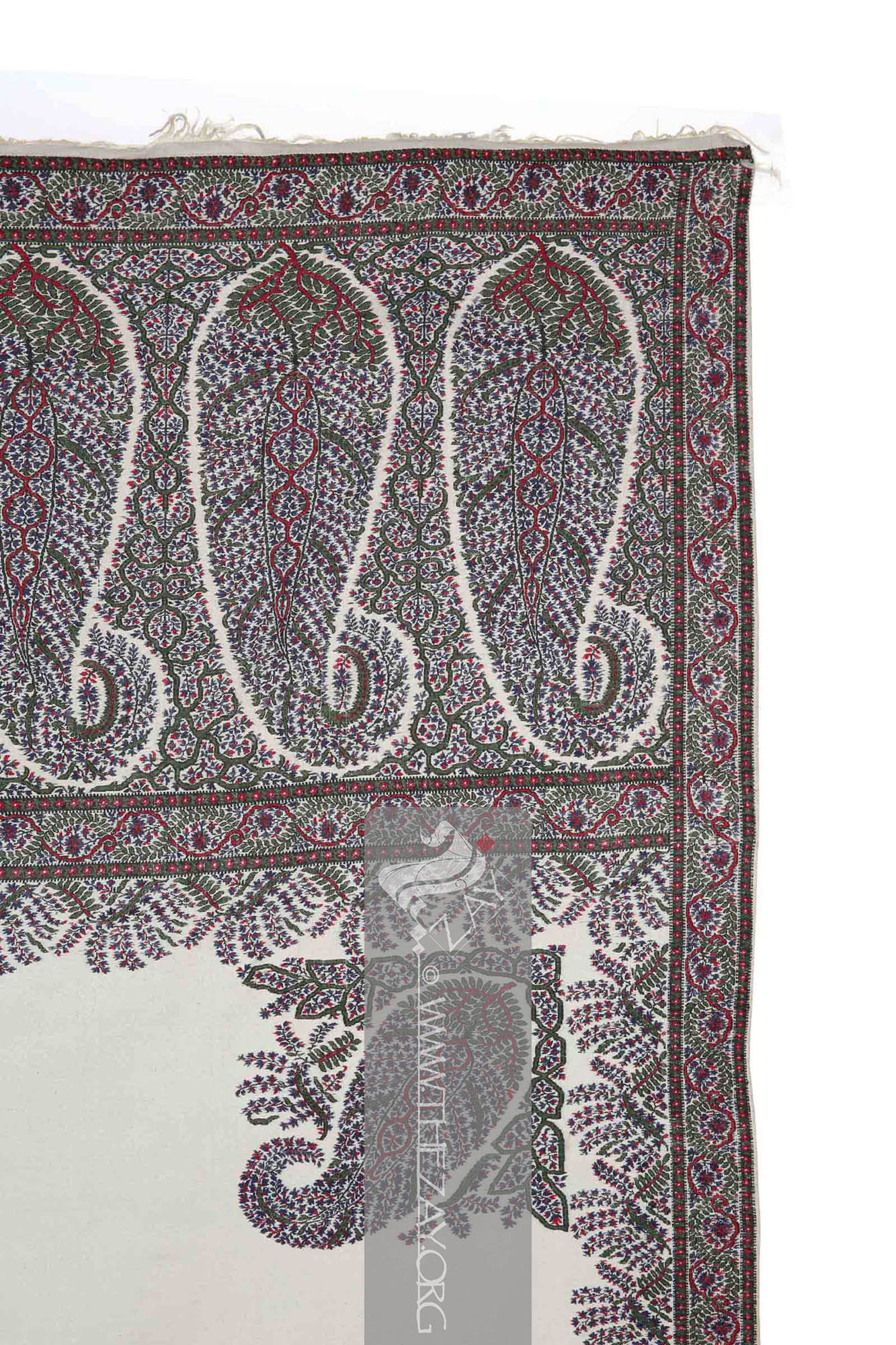
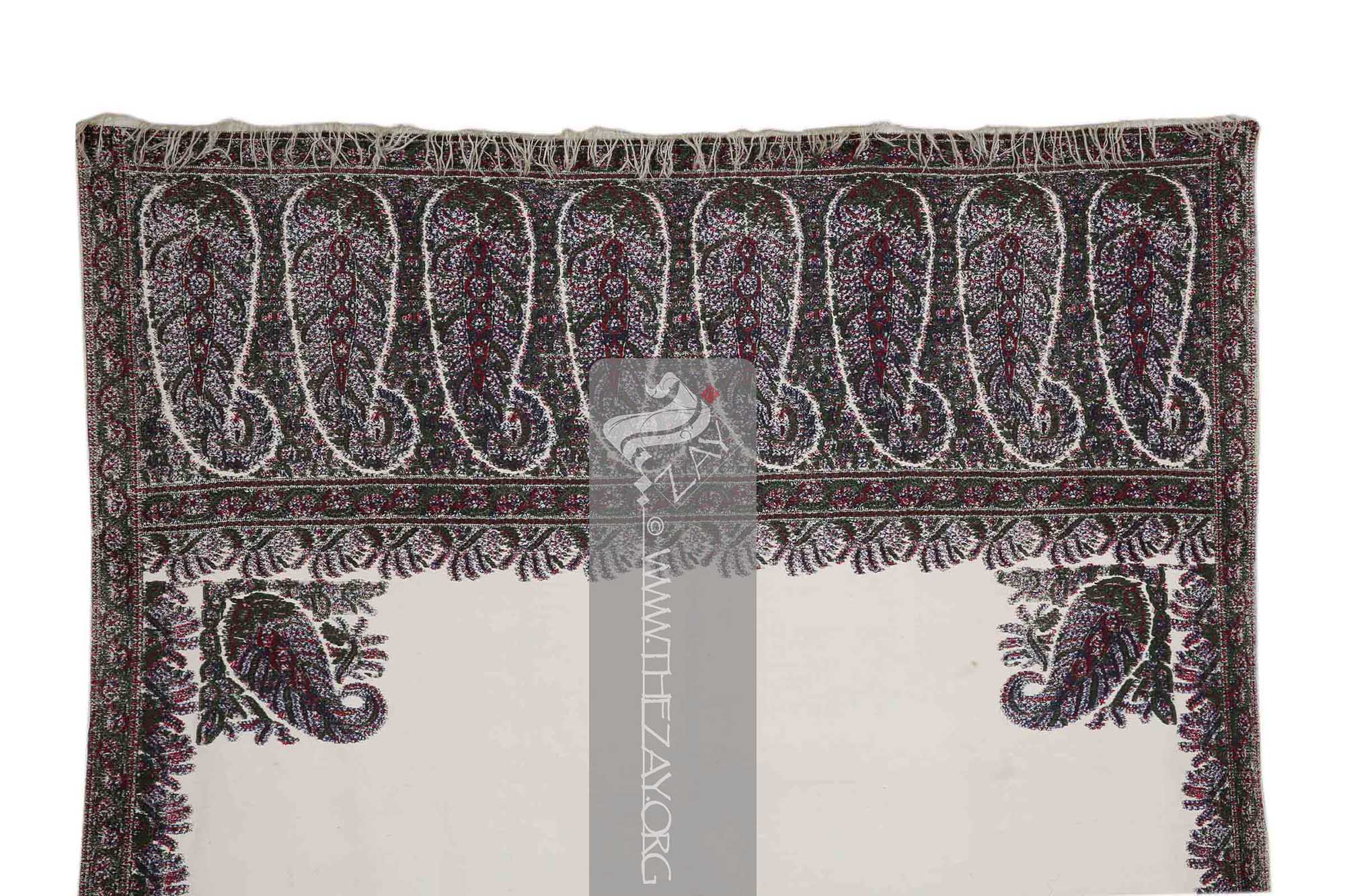
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . ), two pairs of (
tanjir
Tanjīr: (Possibly Persian: zanjir: Chain), a narrow layer of pattern that forms the border and runs above and below the wider layer. ), and a couple of (hashiya). The
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . is filled with eight large floral (
buta
Būta: (Anglicized Persian: boteh – Pinecone shaped motif), known as paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature. in English it is the almond or pinecone-shaped motif, especially in textiles. It is believed to have originated from the Cyprus tree a Zoroastrian symbol for life and eternity. In the current Indian context, however, it simply means motif.)/(pailseys). Each
paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature. has a thin ivory halo around it with sprouting sprigs of foliage in red and bottle green filling its body. The (
jaal
Jaal: (Sanskrit: jaal – A net, web, or a mesh), the decoration which fills the ground between the paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature. cones at the heads of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. .
) of the
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . covering the space between the paisleys is filled with foliage primarily green.
The
tanjir
Tanjīr: (Possibly Persian: zanjir: Chain), a narrow layer of pattern that forms the border and runs above and below the wider layer. and the hashiya are filled with two wavy intertwined vines forming a chain-like pattern in green and red. A tiny red bud embellishes the troughs of the red vines.
A repeat of sprigged foliage runs along the
phala
Phāla: (Etymological origin: Possibly Indo Persian), the wider layer of pattern that forms the border at each warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. end or head of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . and the hashiya framing the central ivory (
matan
Matan: (Arabic, middle of the thing), the main field of a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . ) of the
shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . The four corners of the frame are further decorated with a (
kunjbuta
Kunjbuta: (Sanskrit: kunj – place or corner associated with greenery; and Sanskrit: buta – foliage motif), the word is probably a portmanteau of two Sanskrit words it usually refers to the corner ornaments or decoration on a shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. . ) resting on a (
pai
Pai: (Hindustani: pai – Straight line or base line) The foot or pediment of a buta or a paisley
Paisley: (Scottish Gaelic, Pàislig: a town in Scotland), often called buta, boteh, amli, or kalgi in the subcontinent and kazuwah in Arabic, is a Persian tear drop motif with a curved end specially in textiles. Its popularity and subsequent local production in 18th century at Paisley are responsible for its nomenclature. motif. ) of green foliage tilted in an angle mirroring one another.
A strip of fringes is machine stitched at each (
warp
Warp: One of the two basic components used in weaving which transforms thread or yarns to a piece of fabric. The warp is the set of yarns stretched longitudinally in place on a loom before the weft
Weft: one of the two basic components used in weaving that transforms thread or yarns into a piece of fabric. It is the crosswise thread on a loom that is passed over and under the warp threads. is introduced during the weaving process. ) end to enhance the shawls daintiness and elegance.
It is important to note that long shawls of similar design distribution were in vogue during this period. With high waistlines, flowing skirts, and (
bodice
Bodice: (English: body), or bodices the plural form of body, it is the close-fitting garment meant to cover the body above the waist or the torso. However, it was not until the 17th century that the term became synonymous to women’s undergarment. ) detailing pintucks and wide puff sleeves of women’s dresses in Great Britain during this time large shawls like this were the perfect accessory for a balanced silhouette. By the 1850s with the widening of skirts and (
crinolines
Crinolines: (Latin: crinis – hair, linum – thread, Synonym – Hoop skirt), a hooped or structured petticoat made of a stiff fabric which is composed of horsehair and cotton or linen thread. It was designed to hold a woman’s skirt out and became popular in the 19th century in Europe and the USA.) frames, these shawls became even more popular as it was difficult to wear a jacket or a coat. This resulted in the inclusion of at least one such
shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. in the wedding trousseau of every lady from the aristocracy thus giving rise to the term (
kirking_shawl
Kirking_shawl: (Scottish: Kirk from Old English: cirice – Church; Synonym: Long Shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. ), European versions of and inspired by Kashmiri double shawl
Shawl: (Persian: shāl from Hindi: duśālā – Shoulder Mantle), a shawl is a South Asian version of a scarf worn or wrapped loosely over the shoulders and is usually made of wool. s in wool or silk manufactured locally in Europe. As a part of the trousseau for aristocratic women, it was often used at their first post-wedding church services and christenings. ) especially in Scotland as they were worn to the kirk or church on the first Sunday after the wedding and then again at christenings of children.